
TO STUDY DATA OF E-BANKING
OPERATIONS AT KOTAK MAHINDRA BANK
A Project Submitted to
University of Mumbai for partial completion of the degree of
Bachelor’s in commerce (BANKING & INSURANCE)
Under the Faculty of Commerce
By
HARIT BHATIA
Under the Guidance of
Mr. NIRAV GODA
THAKUR COLLEGE OF SCIENCE AND COMMERCE
Thakur Village, Kandivali (E), Mumbai 400101
APRIL 2021
Certificate
This is to certify that Mr HARIT BHATIA has worked and duly completed his Project Work
for the degree of bachelor’s in commerce
(Banking & Insurance) under the Faculty of Commerce and his project is entitled, “To
STUDY DATA Of E-Banking Operations At Kotak Mahindra Bank” under my supervision.
I further certify that the entire work has been done by the learner under my guidance and that
no part of it has been submitted previously for any Degree or Diploma of any University.
It is his own work and facts reported by his personal findings and investigations.
NAME & NAME &
SIGNATURE OF GUIDE SIGNATURE OF EXTERNAL
Date of submission: 03/04/2021

Declaration by Learner
I the undersigned Mr HARIT BHATIA hereby, declare that the work embodied in this project
work titled “ TO STUDY DATA Of E-Banking Operations At Kotak Mahindra Bank forms
my own contribution to the research work carried out under the guidance of Mr. NIRAV
GODA, result of my own research work and has not been previously submitted to any other
University for any other Degree/ Diploma to this or any other University.
Wherever reference has been made to previous works of others, it has been clearly indicated
as such and included in the bibliography.
I, hereby further declare that all information of this document has been obtained and
presented in accordance with academic rules and ethical conduct.
Name and Signature of the learner
Certified by
Name and signature of the Guiding Teacher
Acknowledgment
I would like to acknowledge the following as being idealistic channels and fresh dimensions
in the completion of this project.
I take this opportunity to thank the University of Mumbai for giving me the chance to do this
project.
I would like to thank my Principal, DR. Mrs. C.T. CHAKRABORTY for providing the
necessary facilities required for completion of this project.
I take this opportunity to thank our Coordinator, _Mr. NIRAV GODA, for his moral support
and guidance.
I would also like to express my sincere gratitude towards my project guide
MR. NIRAV GODA whose guidance and care made the project successful.
I would like to thank my College Library, for having provided various reference books and
magazines related to my project.
Lastly, I would like to thank each and every person who directly or indirectly helped me in the
completion of the project especially my Parents and Peers who supported me throughout my
project.
INDEX
Chapter No.
Title of the Chapter
Page No.
1
Introduction
5-57
2
Research Methodology
58-61
3
Literature Review
62-68
4
Data Analysis
69-76
5
Conclusion
78-78
6
Limitation of Study
78-78
7
Recommendation
78-78
8
Bibliography
79-79

INTRODUCTION
Banks have traditionally been in the forefront of harnessing technology to
improve their products, services and efficiency. They have, over a long time,
been using electronic and telecommunication networks for delivering a wide
range of value-added products and services. The delivery channels include
direct dial – up connections, private networks, public networks etc and the
devices include telephone, Personal Computers including the Automated Teller
Machines, etc. With the popularity of PCs, easy access to Internet and World
Wide Web (WWW), Internet is increasingly used by banks as a channel for
receiving instructions and delivering their products and services to their
customers.
This form of banking is generally referred to as Internet Banking, although the
range of products and services offered by different banks vary widely both in
their Content and sophistication. Broadly, the levels of banking services offered
through INTERNET can be categorized in to three types:
(i) The Basic Level Service is the banks websites which disseminate information
on different products and services offered to customers and members of public
in general. It may receive and reply to customers‟ queries through e-mail.
(ii) In the next level are Simple Transactional Websites which allow customers to
submit their instructions, applications for different services, queries on their
account balances, etc, but do not permit any fund-based transactions on their
accounts
(iii) The third level of Internet banking services are offered by Fully Transactional
Websites which allow the customers to operate on their accounts for transfer of
funds, payment of different bills, subscribing to other products of the bank and
to transact purchase and sale of securities, etc.
The above forms of Internet banking services are offered by traditional banks,
as an additional method of serving the customer or by new banks, who deliver

banking services primarily through Internet or other electronic delivery channels
as the value-added services. Some of these banks are known as “virtual‟ banks
and may not have any physical presence in a country despite offering different
banking services. From the perspective of banking products and services being
offered through Internet. Internet banking is nothing more than traditional
banking services delivered through an electronic communication backbone, viz,
Internet.
But, in the process it has thrown open issues which have ramifications beyond
what a new delivery channel would normally envisage and hence, has compelled
regulators, world over to take note of this emerging channel.

Features Of E-Banking
1. It removes the traditional geographical barriers as it could reach out to
customers of different countries / legal jurisdiction. This has raised the question
of jurisdiction of law / supervisory system, to which such transactions should be
subjected.
2. It has added a new dimension to different kinds of risks traditionally
associated with banking, heightening some of them and throwing new risk
control challenges.
3. Security of banking transactions, validity of electronic contract, customers
privacy, etc., which have all along been concerns of both bankers and
supervisors have assumed different dimensions given that Internet is a public
domain, not subject to control by any single authority or group of users.
4. It poses a strategic risk of loss of business to those banks who do not respond
in time, to this new technology, being the efficient and cost-effective delivery
mechanism of banking services.
5. A new form of competition has emerged both from the existing players and
new players of the market who are not strictly banks. The Regulatory and
Supervisory concerns in e-banking arise mainly out of the distinctive features
outlined above.
These concerns can be broadly addressed under three broad categories, viz
(i) Legal and regulatory issues,
(ii) Security and technology issues and
(iii) Supervisory and operational issues. Legal issues cover those relating to the
jurisdiction of law, validity of electronic contract including the question of
repudiation, gaps in the legal / regulatory environment for electronic commerce.
On the question of jurisdiction, the issue is whether to apply the law of the area
where access to Internet has been made or where the transaction has finally taken
place.

Security of e-banking transactions is one of the most important areas of concerns
to the regulators. Security issues include questions of adopting internationally
accepted state of the art minimum technology standards for access control,
encryption / decryption (minimum key length etc), firewalls, verification of
digital signature, Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) etc. The regulator is equally
concerned about the security policy for the banking industry, security awareness
and education. The supervisory and operational issues include risk control
measures, advance warning system, Information technology audit and re-
engineering of operational procedures. The regulator would also be concerned
with whether the nature of products and services offered are within the
regulatory framework and whether the transactions do not camouflage money-
laundering operations.
The Central Bank may have its concern about the impact of Internet banking on
its monetary and credit policies. As long as Internet is used only as a medium
for delivery of banking services and facilitator of normal payment transactions,
perhaps, it may not impact monetary policy However, when it assumes a stage
where private sector initiative produces electronic substitution of money like e-
cheque, account-based cards and digital coins, its likely impact on monetary
system cannot be overlooked. Even countries where e-banking has been quite
developed, its impact on monetary policy has not been significant. In India, such
concern, for the present is not addressed as the e-banking is still in its formative
stage.

HISTORY OF BANKING SECTOR
Banking in India originated in the last decades of the 18th century. The first
banks were The General Bank of India, which started in 1786, and Bank of
Hindustan, which started in 1790; both are now defunct. The oldest bank in
existence in India is the State Bank of India, which originated in the Bank of
Calcutta in June 1806, which almost immediately became the Bank of Bengal.
This was one of the three presidency banks, the other two being the Bank of
Bombay and the Bank of Madras, all three of which were established under
charters from the British East India Company. For many years, the Presidency
banks acted as quasi-central banks, as did their successors. The three banks
merged in 1921 to form the Imperial Bank of India, which, upon India's
independence, became the State Bank of India.

NATIONALISATION
Despite the provisions, control and regulations of Reserve Bank of India, banks
in India except the State Bank of India or SBI, continued to be owned and
operated by private persons. By the 1960s, the Indian banking industry had
become an important tool to facilitate the development of the Indian economy.
At the same time, it had emerged as a large employer, and a debate had ensued
about the nationalization of the banking industry. Indira Gandhi, then Prime
Minister of India, expressed the intention of the Government of India in the
annual conference of the All-India Congress Meeting in a paper entitled "Stray
thoughts on Bank Nationalization." The meeting received the paper with
enthusiasm. Thereafter, her move was swift and sudden. The Government of
India issued an ordinance and nationalized the 14 largest commercial banks with
effect from the midnight of July 19, 1969. Jayaprakash Narayan, a national
leader of India, described the step as a "masterstroke of political sagacity."
Within two weeks of the issue of the ordinance, the Parliament passed the
Banking Companies (Acquisition and Transfer of Undertaking) Bill, and it
received the presidential approval on 9 August 1969. A second dose of
nationalization of 6 more commercial banks followed in 1980. The stated reason
for the nationalization was to give the government more control of credit
delivery. With the second dose of nationalization, the Government of India
controlled around 91% of the banking business of India. Later, in the year 1993,
the government merged New Bank of India with Punjab National Bank. It was
the only merger between nationalized banks and resulted in the reduction of the
number of nationalized banks from 20 to 19. After this, until the 1990s, the
nationalized banks grew at a pace of around 4%, closer to the average growth
rate of the Indian economy.

POST- INDEPENDENCE
The partition of India in 1947 adversely impacted the economies of Punjab and
West Bengal, paralyzing banking activities for months. India's independence
marked the end of a regime of the Laissez-faire for the Indian banking. The
Government of India initiated measures to play an active role in the economic
life of the nation, and the Industrial Policy Resolution adopted by the
government in 1948 envisaged a mixed economy. This resulted into greater
involvement of the state in different segments of the economy including banking
and finance. The major steps to regulate banking included: The Reserve Bank
of India, India's central banking authority, was nationalized on January 1, 1949
under the terms of the Reserve Bank of India (Transfer to Public Ownership)
Act, 1948 (RBI, 2005b) In 1949, the Banking Regulation Act was enacted which
empowered the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) "to regulate, control, and inspect
the banks in India.

LIBERALISATION
In the early 1990s, the then Narasimha Rao government embarked on a policy
of liberalization, licensing a small number of private banks. These came to be
known as New Generation tech savvy banks and included Global Trust Bank
(the first of such new generation banks to be set up), which later amalgamated
with Oriental Bank of Commerce, Axis Bank (earlier as UTI Bank), ICICI Bank
and HDFC Bank. This move, along with the rapid growth in the economy of
India, revitalized the banking sector in India, which has seen rapid growth with
strong contribution from all the three sectors of banks, namely, government
banks, private banks and foreign banks. The next stage for the Indian banking
has been set up with the proposed relaxation in the norms for Foreign Direct
Investment, where all Foreign Investors in banks may be given voting rights
which could exceed the present cap of 10%, at present it has gone up to 74%
with some restrictions.
The new policy shook the Banking sector in India completely. Bankers, till this
time, were used to the 4-6-4 method (Borrow at 4%; Lend at 6%; Go home at 4)
of functioning. The new wave ushered in a modern outlook and tech-savvy
methods of working for traditional banks. All this led to the retail boom in India.
People not just demanded more from their banks but also received more.
Currently, banking in India is generally mature in terms of supply, product range
and reach-even though reach in rural India still remains a challenge for the
private sector and foreign banks. In terms of quality of assets and capital
adequacy, Indian banks are considered to have clean, strong and transparent
balance sheets relative to other banks in comparable economies in its region.
The Reserve Bank of India is an autonomous body, with minimal pressure from
the government. The stated policy of the Bank on the Indian Rupee is to manage
volatility but without any fixed exchange rate-and this has mostly been true.
With the growth in the Indian economy expected to be strong for quite some
time-especially in its services sector-the demand for banking services, especially

retail banking, mortgages and investment services are expected to be strong.
One may also expect M&As, takeovers, and asset sale.

GROWTH OF BANKING AND DEVELOPMENT IN INDIA
The world’s second largest populated country, India, is the apple of the eye for
the world now. The world economies are seeing it as their potential market. This
has been going on since quite some time now, ever since 1991 reforms of
liberalization, globalization and privatization. Indian markets in urban areas
have grown appreciably and are on the verge of saturation, so corporates have
started tapping rural markets, since more than 60 per cent of India’s population
lives in rural areas. India has been considerably shielded from the global
recession. Firstly, we are not very dependent on the exports for our GDP and
have a good consumer base in India. Secondly, we are a saving prone economy,
unlike western economies which are consumption prone. Thirdly, when banks
across the world are falling like a pyramid of playing cards; we are safe, steady
and strong, with our banks which have acted like a strong backbone of our
economy during present turmoil. And just like the FMCG sector, there is
tremendous growth potential in the banking sector, because firstly, the rural
masses have the habit of saving and spending only when needed. Secondly, their
small credit requirements for agriculture, cottage industry and marriages etc.
According to research carried out by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), on an all
India basis, 59 per cent of the adult population in the country has bank accounts
and 41 per cent don’t. In rural areas, the coverage of banks is 39 per cent, against
60 per cent in urban areas. There is only one bank for a population of 13000.
Within the retail segment, housing loans grew by 20% CAGR during the same
period and consisted ~10% of the total bank credit.
Thus, the banks, which had a big challenge on the unsecured loan front, had at
the same time a bigger opportunity in the mortgage-backed security portfolio.
Abundant liquidity in the banking system during FY10 has been ensured
through secular growth in deposits, low credit demand and prudent borrowing
schedule issued by the government to maintain a balanced growth. According
to a research report, despite the huge borrowings of Rs 4,510 bn by the
government in FY10, the money held in reverse repo by banks remained

considerably high. This will provide an opportunity to the banks to utilize the
money in the most efficient and effective way to the benefit of both the
customers and the economy, comprising various stakeholders. Having talked
about comfortable liquidity and the much-wanted stability in the banking
system, one can expect that bond yields will remain in a higher range and would
not fall significantly.
Other reasons which are likely to support this fact include:
• Lower than expected government borrowings
• Reduced global risk premium
• Higher credit growth. This brings another opportunity for the banks to earn
higher income. Besides the favourable condition for liquidity and high bond
yield, it is expected that the Net Interest Margin (NIM) will not expand much.
The banks need to have higher incremental CD ratio, improvement in spreads
and stable yield on investments to improve NIMs. Banks are expected to have a
low cost of deposits owing to a stable interest rate scenario and ample liquidity
in the system. In the past few years, fee income has been the major contributor
of revenue for private sector banks. Private sector banks have leveraged those
areas to achieve the above, which public sector banks have not been able to, viz.,
transaction- related services and third-party products sales, among others, to
increase this non-fund-based income. Thus, we can very well say that the current
situation has provided a lot of opportunities and challenges to the existing banks.
PORTER’S FIVE FORCES ANALYSIS
1. Threat of New Entrants. The average person cannot come along and start
up a bank, but there are services, such as internet bill payment, on which
entrepreneurs can capitalize. Banks are fearful of being squeezed out of the
payments business because it is a good source of fee-based revenue. Another
trend that poses a threat is companies offering other financial services. What
would it take for an insurance company to start offering mortgage and loan
services? Not much. Also, when analysing a regional bank, remember that the
possibility of a mega bank entering into the market poses a real threat.
2. Power of Suppliers. The suppliers of capital might not pose a big threat, but
the threat of suppliers luring away human capital does. If a talented individual
is working in a smaller regional bank, there is the chance that person will be
enticed away by bigger banks, investment firms, etc.
3. Power of Buyers. The individual does not pose much of a threat to the
banking industry, but one major factor affecting the power of buyers is relatively
high switching costs. If a person has a mortgage, car loan, credit card, checking
account and mutual funds with one particular bank, it can be extremely tough
for that person to switch to another bank. In an attempt to lure in customers,
banks try to lower the price of switching, but many people would still rather
stick with their current bank. On the other hand, large corporate clients have
banks wrapped around their little fingers. Financial institutions - by offering
better exchange rates, more services, and exposure to foreign capital markets -
work extremely hard to get high-margin corporate clients.
4. Availability of Substitutes. As you can probably imagine, there are plenty
of substitutes in the banking industry. Banks offer a suite of services over and
above taking deposits and lending money, but whether it is insurance, mutual
funds or fixed income securities, chances are there is a non-banking financial
services company that can offer similar services. On the lending side of the
business, banks are seeing competition rise from unconventional companies.
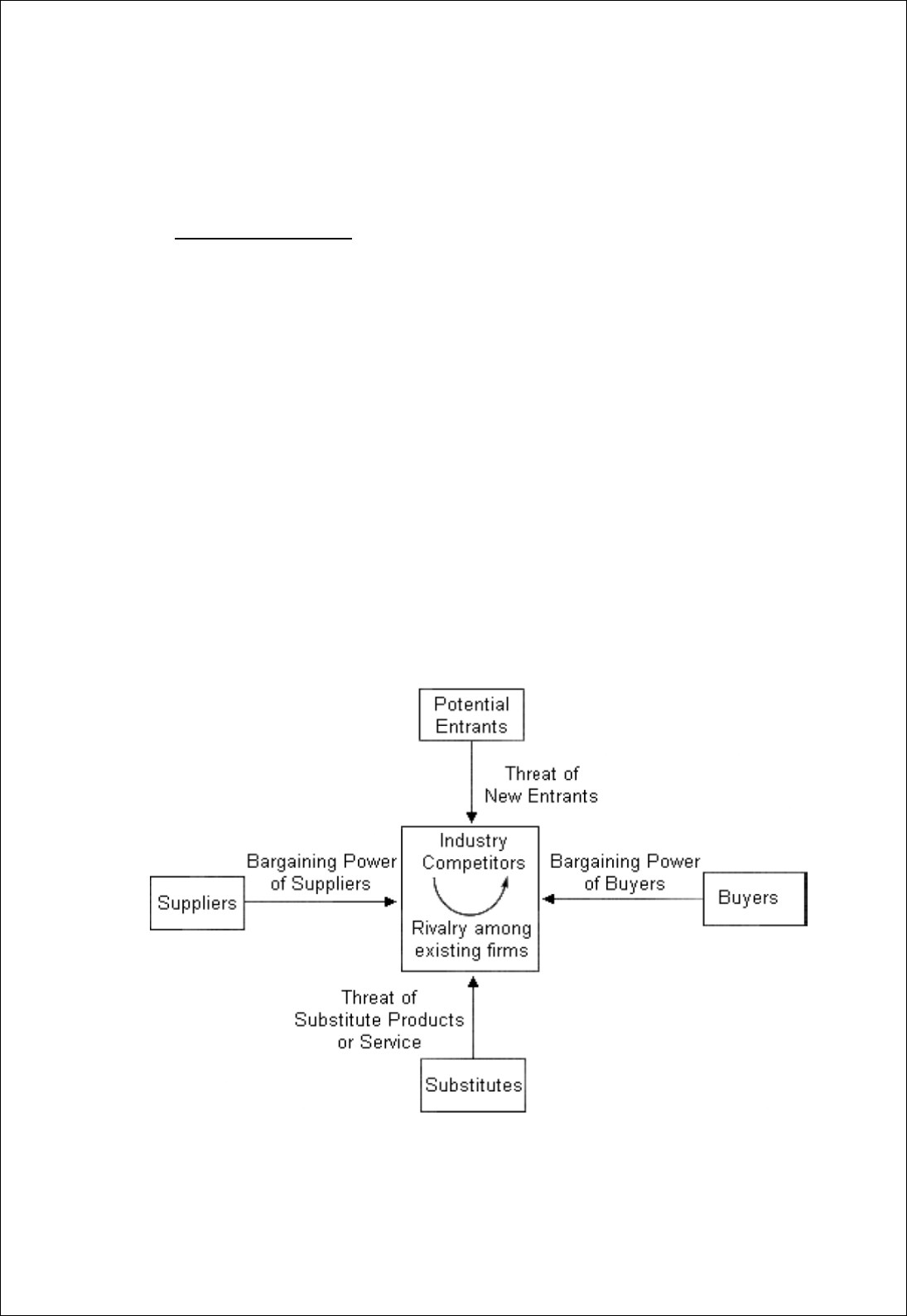
Sony, General Motors and Microsoft all offer preferred financing to customers
who buy big ticket items. If car companies are offering 0% financing, why
would anyone want to get a car loan from the bank and pay 5-10% interest?
5. Competitive Rivalry. The banking industry is highly competitive. The
financial services industry has been around for hundreds of years, and just about
everyone who needs banking services already has them. Because of this, banks
must attempt to lure clients away from competitor banks. They do this by
offering lower financing, preferred rates and investment services. The banking
sector is in a race to see who can offer both the best and fastest services, but this
also causes banks to experience a lower ROA. They then have an incentive to
take on high-risk projects. In the long run, we are likely to see more
consolidation in the banking industry. Larger banks would prefer to take over
on merge with another bank rather than spend the money to market and advertise
to people.

INTRODUCTION OF KOTAK MAHINDRA BANK
Kotak Mahindra Bank is an Indian financial service firm established in 1985. It
was previously known as Kotak Mahindra Finance Limited, a non-banking
financial company. In February 2003, Kotak Mahindra Finance Ltd, the group's
flagship company was given the licence to carry on banking business by the
Reserve Bank of India (RBI). Kotak Mahindra Finance Ltd. is the first company
in the Indian banking history to convert to a bank. Today it has more than 363
branches, 20,000 employees and 10,000 crore in revenue. Mr. Uday Kotak is
Executive Vice Chairman & Managing Director of Kotak Mahindra Bank Ltd.
In July 2011 Mr. C. Jayaram and Mr. Dipak Gupta, whole time directors of the
Bank, were appointed Joint Managing Directors of Kotak Mahindra Bank. Dr.
Shankar Acharya is the chairman of board of Directors in the company. The
Bank has its registered office at Nariman Bhavan, Nariman Point, Mumbai

Kotak Mahindra bank reached the top 100 most trusted brands of India in The
Brand Trust Report published by Trust Research Advisory in 2011.
Kotak Mahindra Bank Ltd Kotak Mahindra Bank Ltd is a one stop shop for all
banking needs. The bank offers personal finance solutions of every kind from
savings accounts to credit cards, distribution of mutual funds to life insurance
products. Kotak Mahindra Bank offers transaction banking, operates lending
verticals, manages IPOs and provides working capital loans. Kotak has one of
the largest and most respected Wealth Management teams in India, providing
the widest range of solutions to high net worth individuals, entrepreneurs,
business families and employed professionals.
Kotak Mahindra Old Mutual Life Insurance Ltd Kotak Mahindra Old Mutual
Life Insurance Ltd is a Company that combines its international strengths and
local advantages to offer its customers a wide range of innovative life insurance
products, helping them take important financial decisions at every stage in life
and stay financially independent. The company covers over 3 million lives and
is one of the fastest growing insurance companies in India Kotak Securities Ltd
Kotak Securities is one of the largest broking houses in India with a wide
geographical reach. Kotak Securities operations include stock broking and
distribution of various financial products including private and secondary
placement of debt, equity and mutual funds. Kotak Securities operate in five
main areas of business: Stock Broking (retail and institutional) Depository
Services Portfolio Management Services Distribution of Mutual Funds
Distribution of Kotak Mahindra Old Mutual Life Insurance Ltd product Kotak
Mahindra Capital Company (KMCC) Kotak Investment Banking (KMCC) is a
full-service investment bank in India offering a wide suite of capital market and
advisory solutions to leading domestic and multinational corporations, banks,
financial institutions and government companies. Our services encompass
Equity & Debt Capital Markets, M&A Advisory, Private Equity Advisory,
Restructuring and Recapitalization services, Structured Finance services and
Infrastructure Advisory & Fund Mobilization Kotak Mahindra Prime Ltd
(KMPL) Kotak Mahindra Prime Ltd is among India's largest dedicated
passenger vehicle finance companies.

KMPL offers loans for the entire range of passenger cars, multi-utility vehicles
and pre-owned cars. Also on offer are inventory funding and infrastructure
funding to car dealers with strategic arrangements via various car manufacturers
in India as their preferred financier. Kotak International Business Kotak
International Business specialises in providing a range of services to overseas
customers seeking to invest in India. For institutions and high net worth
individuals outside India, Kotak International Business offers asset management
through a range of offshore funds with specific advisory and discretionary
investment management services. Kotak Mahindra Asset Management
Company Ltd (KMAMC) Kotak Mahindra Asset Management Company offers
a complete bouquet of asset management products and services that are designed
to suit the diverse risk return profiles of each and every type of investor.
KMAMC and Kotak Mahindra Bank are the sponsors of Kotak Mahindra
Pension Fund Ltd, which has been appointed as one of six fund managers to
manage pension funds under the New Pension Scheme (NPS). Kotak Private
Equity Group (KPEG) Kotak Private Equity Group helps nurture emerging
businesses and mid-size enterprises to evolve into tomorrow's industry leaders.
With a proven track record of helping build companies, KPEG also offers
expertise with a combination of equity capital, strategic support and value added
services.
What differentiates KPEG is not merely funding companies, but also having a
close involvement in their growth as board members, advisors, strategists and
fund-raisers. Kotak Realty Fund Kotak Realty Fund deals with equity
investments covering sectors such as hotels, IT parks, residential townships,
shopping centres, industrial real estate, health care, retail, education and
property management. The investment focus here is on development projects
and enterprise level investments, both in real estate intensive businesses.

VISION STATEMENT
The Global Indian Financial Services Brand
Our customers will enjoy the benefits of dealing with a global Indian brand that
best understands their needs and delivers customized pragmatic solutions across
multiple platforms. We will be a world class Indian financial services group.
Our technology and best practices will be bench-marked along international
lines while our understanding of customers will be uniquely Indian. We will be
more than a repository of our customers' savings. We, the group, will be single
window to every financial service in a customer's universe.
The Most Preferred Employer in Financial Services
A culture of empowerment and a spirit of enterprise attract bright minds with an
entrepreneurial streak to join us and stay with us. Working with a home grown
professionally managed company, which has partnerships with international
leaders, gives our people a perspective that is universal as well as unique.
The Most Trusted Financial Services Company
We will create an ethos of trust across all our constituents. Adhering to high
standards of compliance and corporate governance will be an integral part of
building trust.
Value Creation
Value creation rather than size alone will be our business driver.
THEIR BUSINESSES
Kotak Mahindra Bank Ltd
Kotak Mahindra Bank Ltd is a one stop shop for all banking needs. The bank
offers personal finance solutions of every kind from savings accounts to credit
cards, distribution of mutual funds to life insurance products. Kotak Mahindra
Bank offers transaction banking, operates lending verticals, manages IPOs and
provides working capital loans. Kotak has one of the largest and most respected
Wealth Management teams in India, providing the widest range of solutions to
high net worth individuals, entrepreneurs, business families and employed
professionals.
Kotak Mahindra Old Mutual Life Insurance Ltd
Kotak Mahindra Old Mutual Life Insurance Ltd is a Company that combines its
international strengths and local advantages to offer its customers a wide range
of innovative life insurance products, helping them take important financial
decisions at every stage in life and stay financially independent. The company
covers over 3 million lives and is one of the fastest growing insurance
companies in India
Kotak Securities Ltd
Kotak Securities is one of the largest broking houses in India with a wide
geographical reach. Kotak Securities operations include stock broking and
distribution of various financial products including private and secondary
placement of debt, equity and mutual funds.
Kotak Securities operate in five main areas of business:
Stock Broking (retail and institutional)
Depository Services
Portfolio Management Services
Distribution of Mutual Funds

Distribution of Kotak Mahindra Old Mutual Life Insurance Ltd products
Kotak Mahindra Capital Company (KMCC)
Kotak Investment Banking (KMCC) is a full-service investment bank in India
offering a wide suite of capital market and advisory solutions to leading
domestic and multinational corporations, banks, financial institutions and
government companies. Our services encompass Equity & Debt Capital
Markets, M&A Advisory, Private Equity Advisory, Restructuring and
Recapitalization services, Structured Finance services and Infrastructure
Advisory & Fund Mobilization
Kotak Mahindra Prime Ltd (KMPL)
Kotak Mahindra Prime Ltd is among India's largest dedicated passenger vehicle
finance companies. KMPL offers loans for the entire range of passenger cars,
multi-utility vehicles and pre-owned cars. Also on offer are inventory funding
and infrastructure funding to car dealers with strategic arrangements via various
car manufacturers in India as their preferred financier.
Kotak International Business
Kotak International Business specialises in providing a range of services to
overseas customers seeking to invest in India. For institutions and high net worth
individuals outside India, Kotak International Business offers asset management
through a range of offshore funds with specific advisory and discretionary
investment management services.
Kotak Mahindra Asset Management Company Ltd (KMAMC)
Kotak Mahindra Asset Management Company offers a complete bouquet of
asset management products and services that are designed to suit the diverse risk
return profiles of each and every type of investor. KMAMC and Kotak
Mahindra Bank are the sponsors of Kotak Mahindra Pension Fund Ltd, which
has been appointed as one of six fund managers to manage pension funds under
the New Pension Scheme (NPS).

Kotak Private Equity Group (KPEG)
Kotak Private Equity Group helps nurture emerging businesses and mid-size
enterprises to evolve into tomorrow's industry leaders. With a proven track
record of helping build companies, KPEG also offers expertise with a
combination of equity capital, strategic support and value added services. What
differentiates KPEG is not merely funding companies, but also having a close
involvement in their growth as board members, advisors, strategists and fund-
raisers.
Kotak Realty Fund
Kotak Realty Fund deals with equity investments covering sectors such as
hotels, IT parks, residential townships, shopping centres, industrial real estate,
health care, retail, education and property management. The investment focus
here is on development projects and enterprise level investments, both in real
estate intensive businesses.
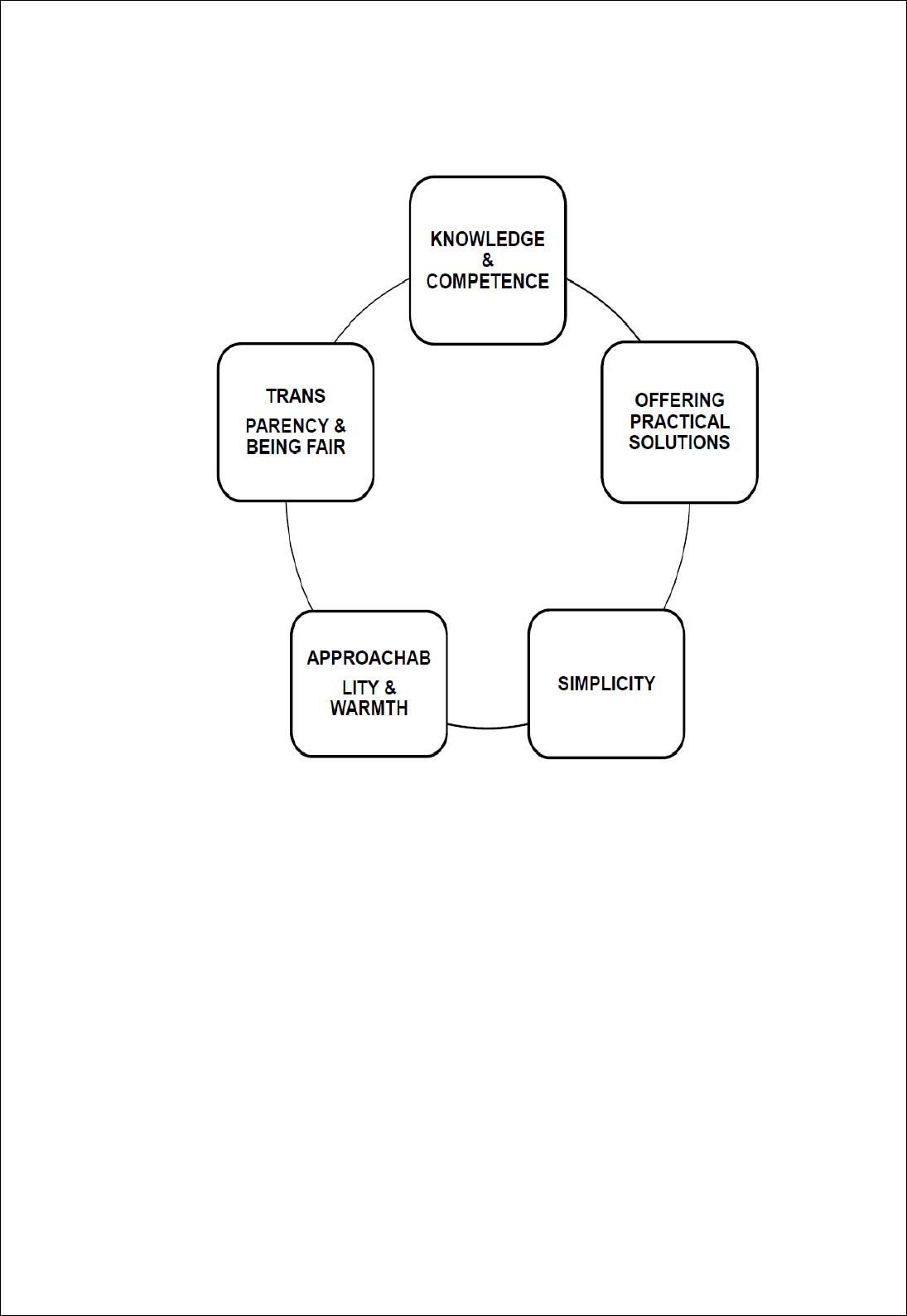
KOTAK’S SPIRIT OF SERVICE

The launch of SPIRIT OF SERVICE QUALITY INITIATIVE has ignited a
renewed sense of service at Kotak bank. It is a new mantra that takes spirit to
great heights. The above 5 pillars help to incorporate it.
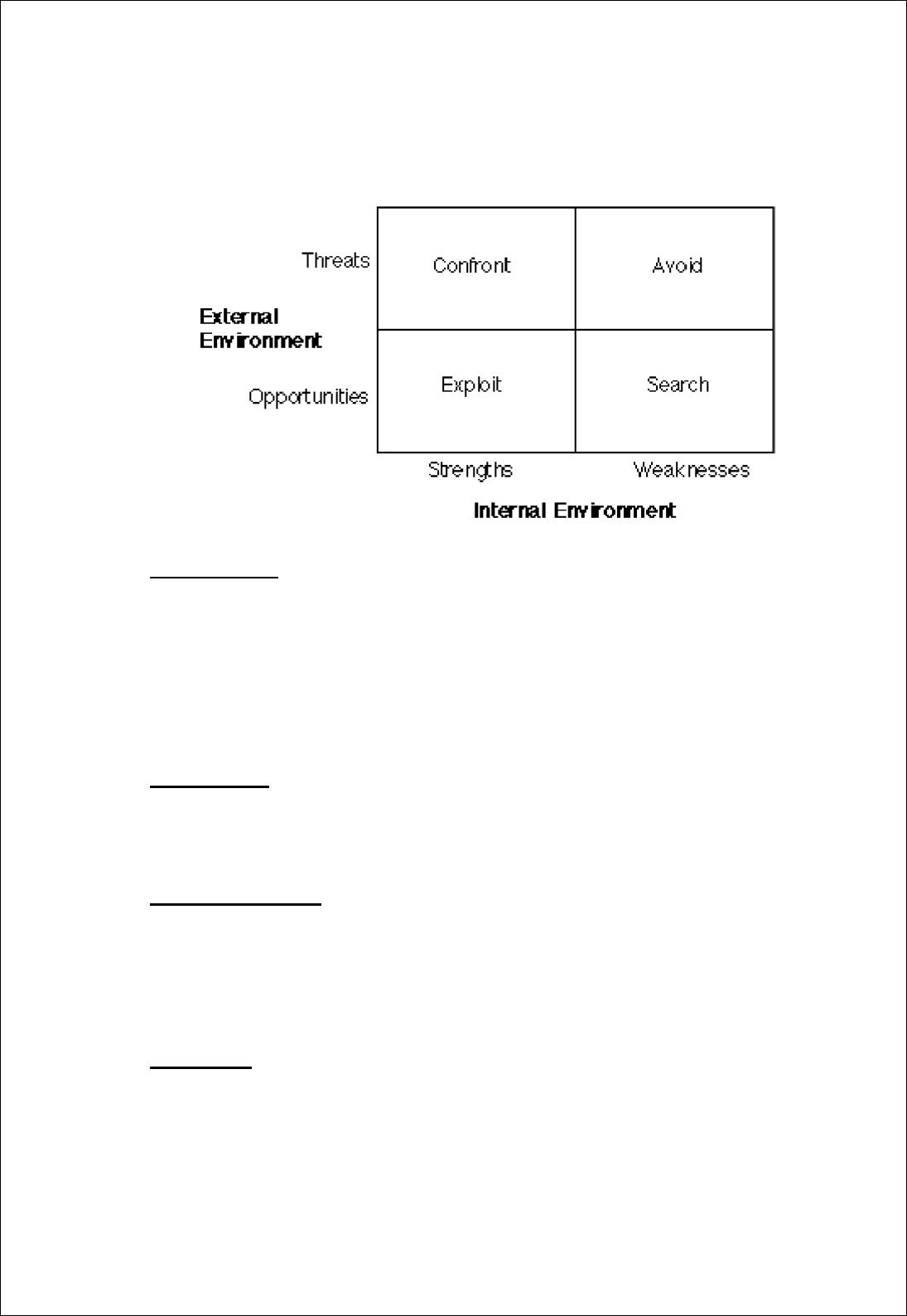
SWOT ANALYSIS OF KOTAK MAHINDRA BANK
STRENGHTS:
1) Innovative financial product of diverse categories
2) Kotak Mahindra Finance Ltd. is the first company in the Indian banking
history to convert into a bank
3) Of, For, By the customers
4) Has over 20,000 employees
5) Customer account base of over 2.7 million
WEAKNESS:
1) Low publicity and marketing as compared to other premium banks in the
urban area
OPPORTUNITIES:
1) Explore opportunities abroad by International banking
2) Kotak has launched SPIRIT OF SERVICE campaign. Through this
campaign it can secure higher and higher levels of CUSTOMER
SATISFACTION, LOYALTY ETC.
THREATS:
1) Heavy weight corporate like TATA & SONS, RELIANCE CAPITAL,
L&T, ADITYA BIRLA, BAJAJ FINSERV, and MUTHOOT FINANCE are
trying very hard and leaving no stone unturned to acquire banking license
2) Competitors: ICICI, SBI, AXIS, BOB, HSBC etc.
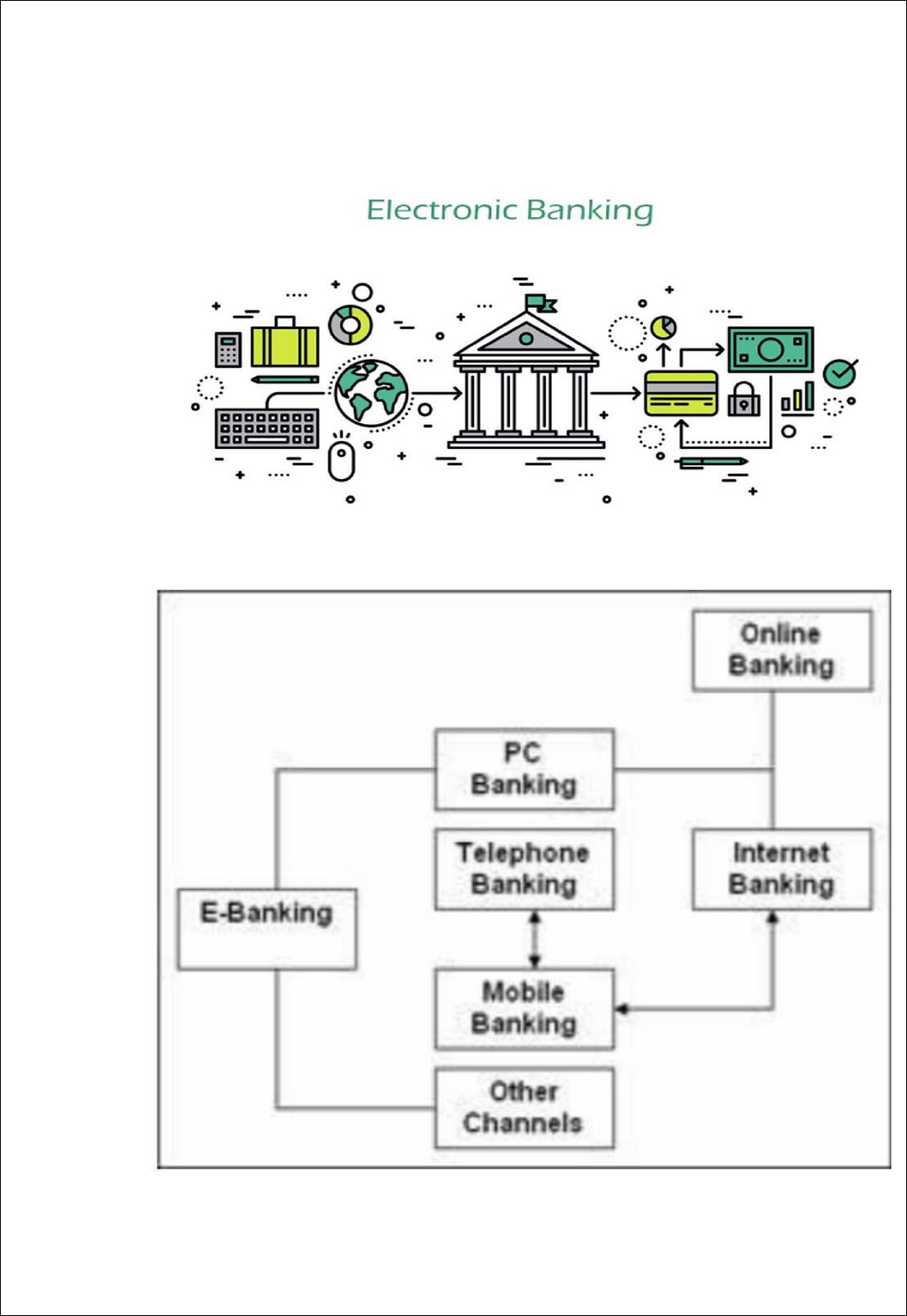
E-BANKING IS ELECTRONIC BANKING

“Internet banking (or E-banking) means any user with a personal computer and
a browser can get connected to his banks website to perform any of the virtual
banking functions. In internet banking system the bank has a centralized
database that is web enabled”.

E-BANKING SERVICES & PRODUCTS
Internet banks offer a variety of features and perks, rushing to lure online
customers. The race is on to increase market share and creates customer loyalty
with features that make online banking friendlier, more useful, and less
expensive. E-Banking lures customers with convenience.
THE THREE BROAD FACILITIES THAT E-BANKING OFFERS ARE:
• Convenience- Complete your banking at your convenience, in the comfort of
your home or at any place you can access the Net
• No more Qs - There are no queues at an online bank
• 24/7 service- Bank online 24 hours a day, 7 days a week and 52 weeks a year
Below is a detailed review of features found in Internet banking around the
world.
ONLINE APPLICATIONS:
Consumers can begin their banking relationship with an online application. No
need to waste time driving to a local branch to begin a banking relationship.
Consumers can fill out and submit electronically all necessary information
needed to open a checking, savings account or even a fixed deposit. When the
application is submitted, the bank will mail you a signature card for its records
and request you to mail or wire your initial funds. Firms like American Express
enable customers applying for an account to fund their new account
electronically via a credit card or cheque from another banking institution. There
are some firms such as Wingspan and USA BancShares.com that enable
customers to digitally sign their applications.
ACCOUNT ACCESS:
Internet banking customers now have the ability to view their accounts online,
including checking, savings, loans and credit cards. No need to wait for your
monthly statements or wait in queue for the next available customer service
representative. Account access enables customers to view most recent activity
on accounts, including cleared checks, deposits, ATM transactions and balances
as of previous day’s activities. Customers no longer have to hold on to the
cleared checks, since their bank will store them for them online.
ACCOUNT TRANSFERS:
Internet banking customers have the ability to transfer funds to and from their
accounts online. With a simple online form, customers can move money from a
checking account to a savings account and vice versa within the safety and
convenience of their home without having to visit the ATM. Funds transferred
online are updated in less than three hours. In addition, customers can set up

recurring transfers to accounts. A recurring transfer will take place on the
customer specified date, with a specified amount.
BILL PAYMENT:
Online bill payment enables customers to pay anyone, friends or family, as well
as a pay their bills electronically. As an add on feature to Internet banking, bill
payment enables customers to send paper checks to anyone or an electronic
check to any institution that accepts electronic bill payments. To use bill
payment, customers are required to set up their payees online. Customers then
have the ability to set up recurring, automatic payments to a specific biller on a
specified day or just a one-time payment. Arrange payments three to five days,
before the due date, to ensure timely delivery. It is important to note that not all
banks provide bill payment as a free feature
AUTOMATED TELLER MACHINE:
ATM is designed to perform the most important function of bank. It is operated
by plastic card with its special features. The plastic card is replacing cheque,
personal attendance of the customer, banking hour’s restrictions and paper based
verification. There are debit cards. ATMs used as spring board for Electronic
Fund Transfer. ATM itself can provide information about customers account
and also receive instructions from customers - ATM cardholders. An ATM is
an Electronic Fund Transfer terminal capable of handling cash deposits, transfer
between accounts, balance enquiries, cash withdrawals and pay bills. It may be
on-line or off-line. The on-line ATN enables the customer to avail banking
facilities from anywhere. In off-line the facilities are confined to that particular
ATM assigned. Any customer possessing ATM card issued by the Shared
Payment Network System can go to any ATM linked to Shared Payment
Networks and perform his transactions.
CREDIT-DEBIT CARD:
The Credit Card holder is empowered to spend wherever and whenever he wants
with his Credit Card within the limits fixed by his bank. Credit Card is a post-
paid card. Debit Card, on the other hand, is a prepaid card with some stored
value. Every time a person uses this card, the Internet Banking house gets money
transferred to its account from the bank of the buyer. The buyers account is
debited with the exact amount of purchases. An individual has to open an
account with the issuing bank which gives debit card with a Personal
Identification Number (PIN). When he makes a purchase, he enters his PIN on
shops PIN pad. When the card is slurped through the electronic terminal, it dials
the acquiring bank system - either Master Card or VISA that validates the PIN
and finds out from the issuing bank whether to accept or decline the transactions.
The customer can never overspend because the system rejects any transaction
which exceeds the balance in his account. The bank never faces a default
because the amount spent is debited immediately from the customer’s account.

SMART CARDS:
Banks are adding chips to their current magnetic stripe cards to enhance security
and offer new service, called Smart Cards. Smart Cards allow thousands of times
of information storable on magnetic stripe cards. In addition, these cards are
highly secure, more reliable and perform multiple functions. They hold a large
amount of personal information, from medical and health history to personal
banking and personal preferences. Apart from this ALERTS, SMS BANKING,
MOBILE BANKING, PHONE BANKING, are also part of E-banking.

BENEFITS OF E-BANKING
24/7 CUSTOMER SERVICE:
Although it is easy to yield to the temptation of allowing the Internet to replace
expensive branch personnel and overhead, many banks have found that an
customer service staff ready at any hour is well worth the expense. This can be
especially true as customer’s transition to online banking and need help learning
the features. Offering telephone and email contacts are a basic level of service.
Offering live chat assistance is the exceptional level.
ACCESS TO OLD TRANSACTIONS:
Choices made in designing the Internet interface may include how much history
will be available online. Some banks have chosen to show only 30-45 days,
while others offer a history of six months or a year.
CATEGORIZE TRANSACTIONS AND PRODUCE REPORTS:
Functionality is king as online banking customers using these features enjoy a
Web interface that delivers the utility of a money management software
application.
EXPORT YOUR BANKING DATA:
Most banks offering the management interface also allow easy downloading of
financial information into files that can be imported into Microsoft Money and
Intuit's Quicken.
INTERACTIVE GUIDES & TOOLS TO HELP SELECTION OF
PROPER PRODUCT:
Although online, interactive guides through a bank's products, adds complexity
to the programming it also serves the bank by assisting potential customers in
choosing new products or services. Interactive Tools to design a savings plan,
choose a mortgage, obtain online insurance quotes all tied to applications These
tools help remove some of the mystery involved in so many account options and
costs.
LOAN STATUS AND CREDIT CARD ACCOUNT INFORMATION:
Bank customers are familiar with reviewing their checking account information,
but many banks are adding the ability to look at one's loan status and credit card
information as well. Access to as many accounts held at the bank seems to be
the goal.
VIEW DIGITAL COPIES OF CHECKS:
This, again, is removing a down side to online banking. It makes images of
checks available as replacement for sending out cancelled checks or sheets of
printed check images.
ONLINE FORMS FOR ORDERING CHECKS, STOP PAYMENT, ETC.
Convenience is popular and if a customer visits his or her online account
frequently it only makes sense to allow the ability to reorder checks or perform

certain other commands through the same interface. These features and many
others help customers save time, simplify their lives and provide greater value
than conventional banking.

E- BANKING THREATS FACED BY INDIVIDUALS
1) HACKING: Hacking means finding out weaknesses in an established system
and exploiting them. A computer hacker is a person who finds out weaknesses
in the computer and exploits it. Hackers may be motivated by a multitude of
reasons, such as profit, protest, or challenge. The subculture that has evolved
around hackers is often referred to as the computer underground, but it is now
an open community.
2) VIRUSES: Computer Virus is a malicious software program written
intentionally to enter a computer without the user's permission or knowledge. It
has the ability to replicate itself, thus continues to spread. Some viruses do little
but replicate, while others can cause severe harm or adversely affect program
and performance of the system. A virus should never be assumed harmless and
left on a system.
3) DENIAL-OF-SERVICE ATTACK (DOS): A denial-of-service attack (DOS
attack) or distributed denial-of-service attack (DOS attack) is an attempt to make
a computer or network resource unavailable to its intended users. Although the
means to carry out, motives for, and targets of a DOS attack may vary, it
generally consists of the concerted efforts of a person, or multiple people to
prevent an Internet site or service from functioning efficiently or at all,
temporarily or indefinitely. Perpetrators of DOS attacks typically target sites or
services hosted on high-profile web servers such as banks, credit card payment
gateways, and even root name servers. One common method of attack involves
saturating the target machine with external communications requests, such that
it cannot respond to legitimate traffic, or responds so slowly as to be rendered
effectively unavailable. Such attacks usually lead to a server overload. In
general terms, DOS attacks are implemented by either forcing the targeted
computer(s) to reset, or consuming its resources so that it can no longer provide
its intended service or obstructing the communication media between the
intended users and the victim so that they can no longer communicate
adequately. When the DOS Attacker sends many packets of information and
requests to a single network adapter, each computer in the network would
experience effects from the DOS attack.
4) IDENTITY THEFT: It is a form of stealing another person's identity in which
someone pretends to be someone else by assuming that person's identity,
typically in order to access resources or obtain credit and other benefits in that
person's name. The victim of identity theft (here meaning the person whose
identity has been assumed by the identity thief) can suffer adverse consequences
if they are held accountable for the perpetrator's actions. Organizations and
individuals who are duped or defrauded by the identity thief can also suffer
adverse consequences and losses, and to that extent are also victims.
5) PHISHING: It is a way of attempting to acquire information such as usernames,
passwords, and credit card details by masquerading as a trustworthy entity in an

electronic communication. Communications purporting to be from popular
social web sites, auction sites, online payment processors or IT administrators
are commonly used to lure the unsuspecting public. Phishing is typically carried
out by e-mail spoofing or instant messaging and it often directs users to enter
details at a fake website whose look and feel are almost identical to the
legitimate one. Phishing is an example of social engineering techniques used to
deceive users, and exploits the poor usability of current web security
technologies.
6) SPAM: Spam is the use of electronic messaging systems (including most
broadcast media, digital delivery systems) to send unsolicited bulk messages
indiscriminately. While the most widely recognized form of spam is e-mail
spam, the term is applied to similar abuses in other media: instant messaging
spam, Usenet newsgroup spam, Web search engine spam, spam in blogs, wiki
spam, online classified ads spam, mobile phone messaging spam, Internet forum
spam, junk fax transmissions, social networking spam, television advertising
and file sharing network spam. The spam messages in India are about 3.6 trillion
per year.
7) KEY LOGGING: Software implanted in the customer's computer that records
all the keystrokes of the customer, providing a complete record of user IDs,
passwords, pin codes, account numbers and transactions. Sometimes this is
integrated with additional rogue software, and usually it sends the information
it has collected to the hacker.
8) PHARMING: It is a hacker's attack aiming to redirect a website's traffic to
another, bogus website. Pharming can be conducted either by changing the hosts
file on a victim’s computer or by exploitation of a vulnerability in DNS server
software. In January 2008, Symantec reported a drive-by pharming incident
directed against a Mexican bank in which the DNS settings on a customer's
home router were changed after receipt of an e-mail that appeared to be from a
legitimate Spanish-language greeting card company.
9) CROSS-SITE SCRIPTING (XSS): It is a type of computer security
vulnerability typically found in Web applications that enables attackers to inject
client-side script into Web pages viewed by other users. A cross-site scripting
vulnerability may be used by attackers to bypass access controls such as the
same origin policy.
10) COOKIE POISONING: Cookie Poisoning attacks involve the modification of
the contents of a cookie (personal information stored in a Web user's computer)
in order to bypass security mechanisms. Using cookie poisoning attacks,
attackers can gain unauthorized information about another user and steal their
identity.

E-BANKING FRAUD CASES IN INDIA
1] YOUTH ARRESTED FOR NET-BANKING FRAUD
MUMBAI: A 23-year-old, who had opened a fictitious account and siphoned off Rs 4 lakh
through net-banking, was arrested by the cyber police station on Monday. Pradeep Kanere was
picked up after the Bank of Baroda tipped off the cyber police officials that a person who had
an account that was under surveillance had come to the bank.
Kanere has been charged with cheating and forgery and cops are looking for his associates who
have withdrawn a huge amount from a private company using a similar modus operandi. The
complaint was filed by Kayesh Shah of Energy Park Boilers Private Limited. Shah told police
that the company had an account with the Bank of Baroda and the bank had given him net-
banking facility. His brothers, Uday and Kartik, were also directors of the company but only
he had access to the net-banking password, he added
.
Recently, while he was going through the account statement, he was shocked to see some
transactions that he never done. "Between August 10 and August 18, around Rs 3.92 lakh was
withdrawn through net-banking,'' a police officer said. Shah immediately brought it to notice
of bank officials who started probing the accounts where the amount was credited.
Shah also approached the cyber police station at Bandra-Kurla Complex and lodged a
complaint. Kanere walked into the bank's Vile Parle branch on Monday, saying he had lost an
ATM card and needed to close the accounts. "The bank officials kept him engaged in
documentation and informed the police. Officials are trying to trace his associates and find out
how he decoded the password,'' an official said.
2] POLICE PROBE INTERNET BANKING FRAUD
KHAR: Police is probing an internet banking fraud to the tune of Rs 68,000, allegedly by a
Delhi-based hacker, police said. "Anil Bansal, in his complain to the police, said that his wife's
account in a private bank was hacked within a span of two days on June 21 and 22 of Rs
68,000," police said.
"Bansal, also carried out his own investigations and found that one Ganesh Agrawal staying in
Kirti Nagar, Delhi had allegedly made these transactions," police said, and added that the
detective crime branch was gathering all details about the accused.
3] NIGERIAN 'KINGPIN' ARRESTED IN MULTI-CRORE ONLINE BANKING
FRAUD
KOLKATA: Beware before clicking a mail sent by any unknown person. You could be a victim
of 'sphygmograph' - a hi-tech e-fraud - and within days fraudsters may empty your bank
account. On Thursday the anti-bank fraud squad of Kolkata Police, led by Soumya Banerjee,
unearthed a racket operated by group of Nigerians. One of the kingpins, Felix Nudubisieigs,
has been arrested from Puduchhery, say police. Investigators say that Felix, who has been in

India since 2006, is one of the masterminds of the racket which has swindled crores of rupees
from people in the last year alone.
In the past few months Kolkata Police has been receiving peculiar complaints from people that
their money has been withdrawn or transferred to some unknown account. Alind Jain was one
among the victims. A resident of Moradabad, he said that Rs 40,000 was withdrawn from his
account and transferred to an account of private bank at Shakespeare Sarani. He suspected his
e-banking password had been compromised but could not say how.
Investigators were stunned when they finally unravelled the modus operandi. The scamsters
used to send lucrative mails randomly across the country. The mails could be in different forms.
You could get a job offer from a multinational company. Or a lottery or even a greetings. When
a recipient clicked on the mail, a Trojan virus would penetrate their system.
It remains dormant when the victim logs out of the mail account. When he logs back in, the
virus starts copying every stroke on the keyboard and the details of the mail and sends to the
mother server operated by the fraudsters.
Investigators said that soon after getting the copied details, the fraudsters start monitoring the
victim's mail. If he logs into his bank account online to check his balance, the racketeers get
every detail, including the password. If the victim's account balance is lucrative then transfer
the money to another account opened in a fictitious name. The racket was so smart that
businessmen were conned into paying directly into the fraud account. For instance, if someone
got a mail from his business partner for a payment, the fraudsters would spy on it and use the
stolen details to send a fake mail asking that the money be deposited in such and such account.
Police said that the clever fraudsters recruited scores of Indians to open account in fictitious
names to conceal the direct involvement of the Nigerians. They asked the recruited youths to
open as many accounts in different banks as they could. "The foot soldiers got a cut of the
amount transferred to the account. Soon after a few fraudulent transactions, the gang used to
ask the account holder to shut it and open another one," said an officer. The racket generally
used routed each fraud transaction through five to six accounts before withdrawing the money.
Investigators have spotted more than 20 such accounts in Tripur, Chennai and other cities in
south India. Police have sealed several accounts containing crores of rupees swindled from
different people across the country India and are now looking for the victims. Felix landed in
India on a student visa and later joined the fraud racket, said police. "He was produced before
a Tripur court on Thursday and will be bring to Kolkata on transit remand," said joint
commissioner of police, crime, Damayanti Sen
4] CHARTERED ACCOUNTANT LOSES RS 1.41 LAKH IN NET BANKING FRAUD
A chartered accountant employed with a Gurgaon-based MNC and resident of VasantKunj in
New Delhi alleged that he was fleeced of Rs.1.31 lakh through internet banking fraud.
According to victim Harsh Mehta, 27, the money was siphoned off from his salary account in
the Gurgaon branch of Standard Chartered Bank. He also claimed to have lost Rs 10,654 on
his credit card.
Shuttling between Delhi and Gurgaon to get a police complaint registered since Friday, the

KPMG employee said his phone was first hacked and a onetime password (OTP) obtained from
the bank. A case is yet to be registered and Mehta claimed that neither the mobile company nor
the bank is helping him. I do use internet banking but such a thing has never happened before.
The hacker also got the bank SMS alert service deactivated, so I could not get messages
notifying me of transactions,” Mehta claimed. On January 19 around 5 pm, I received an
SMS from Airtel giving an ID for changing my SIM number.
After that, there was no signal on my mobile. I was surprised as I had never made such a
request. I contacted the Airtel customer care officer and he assured me that nothing would
happen and they will keep a check,” he said. The next morning, I received an email from the
bank showing unknown transactions to the tune of Rs.1.31 lakh. The accused must have hacked
my phone first, requested the bank for OTP, activated my SIM on his phone and then
transferred funds to his account. As the bank limit was of Rs.1 lakh per day, the accused
transferred the amount till midnight.
After that, he shifted the remaining balance of Rs 31,000. My credit card was also used for
Rs.10,650, the victim added.
5] ENGINEERING STUDENT LOSES RS 5 LAKH: SMS FRAUD
An engineering student here lost Rs 5 lakh to SMS fraudsters who lured him by promising Rs
5.5 crore lottery money. According to police, the student received the message on his mobile
stating that he had won 7 lakh Sterling Pounds (around Rs 5.5 Crore) and he had to pay Rs
5,10,399 to receive price money.
He paid the entire amount in three instalments. After the payment, the sender of the SMS went
incommunicado. Based on a complaint filed by the student, the Madurai City Central Crime
Branch registered a case. Police has advised the people not to get fooled by such SMS. They
also warned people against disclosing bank account numbers to strangers.
6] VODAFONE TO RETURN RS 59,000 TO NET BANKING FRAUD VICTIM
Though Vodafone has returned about Rs 59,000 in net banking fraud case after three months,
but the real culprit who made the transactions one after the other using different Internet
Protocol (IP) addresses is yet to be identified and arrested.
On May 13, Pawan Kumar Singhal, a resident of Sector 11, complained to the police that a sum
of Rs 98,000 had been fraudulently withdrawn on the intervening night from his IDBI account
through net banking. The account contained around Rs 3 lakh.
On learning about the fraud, he immediately informed the bank’s office at Mumbai to close net
banking facility. Singhal retired as General Manager of Haryana Dairy in 2005 and now has
been working as a chartered accountant.
The police registered the FIR on May 20 under Section 406 (for criminal breach of trust), 420
and relevant sections of Cyber Act. As per information provided by IDBI bank to the police,
the money was withdrawn through 28 transactions, each of Rs 3,500, and deposited in 28
Vodafone customers‟ accounts. The bank had also informed that the transactions were made
through 90 IP addresses, which failed in some cases too.

The Panchkula police further wrote to Vodafone about closing the accounts, but it was too late
by then. The company was able to save about Rs 59,000, which was returned to the police
through a cheque. The cheque has come in the name of investigating officer instead of the
complainant. So the police is planning to send it back with a request to reissue it in Singhal’s
name.

E-BANKING: PRECAUTIONS
1) CHANGE YOUR PASSWORD REGULARLY: Users must change their
password after the first log-in for online banking. Besides, keep changing your
password at regular intervals. Needless to say, don't disclose your password to
anyone, not even the banking staff.
2) AVOID USING CYBER CAFES FOR BANKING PURPOSES: Avoid
using the Internet banking facility from cyber cafes, libraries or from systems
installed in public places. But in case it is an absolute necessity, you must clear
the browser cache and delete the temporary files on the PC you've accessed the
Internet from.
3) DON'T USE PERSONAL DETAILS IN THE PASSWORD: Avoid using
your date of birth, telephone number, address or name in your password. This
practice makes your account more vulnerable to being hacked as your password
can be easily guessed by just about anyone. Besides, do not leave your computer
unattended while you are logged in to the bank site.
4) DON’T LET YOUR BROWSER MEMORIZE YOUR DETAILS: Never
let your computer remember your passwords, names, etc. Always disable the
browser's option of storing usernames and passwords.
5) DON'T E-MAIL CREDIT CARD AND ACCOUNT DETAILS: Make it a
thumb rule not to send credit card or account details via e-mail to anybody, or
in response to an e-mail.
6) SHOP AT REPUTED SITES ONLY: While shopping online, please wait for
a second and check if the website is an established one and a reputed name in
the online shopping domain. Always check if the shopping site has a well
established permanent address.
7) LOG OFF WHEN FINISHED: Always log off after Internet banking once
you are done with it. You need to log out from the website and do not shut off
the window in order to log off from the session.
8) CHECK THE ACCOUNT: Whenever you make a transaction, immediately
check your account and see if the right amount has been deducted or added to
it. In case there is any misappropriation, inform the concerned bank
immediately.
9) DON'T FOLLOW THE LINKS: Always reject any e-mail that asks you to
follow a link to the website of your bank. You may end up revealing your
personal details on a fake bank website, from which hackers steal information.
10) DESTROY THE RECEIPTS: Do not keep documents and receipts related to
your online translations. They usually carry confidential personal financial
information. You had better destroy or shred such documents or receipts to stop
them from falling into the wrong hands.

11) DON'T SHARE YOUR PERSONAL INFORMATION ON WEBSITES:
You shouldn't give your e-mail address at websites without knowing how it will
be used. Besides, do not share your personal information like date of birth, etc,
on the Internet unnecessarily because it can be used by others to unlock or
generate your account password.

SWOT ANALYSIS OF E-BANKING
STRENGHTS:
• Customer access to information 24 hours a day
• Timely access to information
• Ability to offer a customer more than one method of retrieving information
• Sophisticated technology systems
• Diversity helps to capture different types of market.
• The ability to cut internal cost due to advanced technology
• Increased efficiency due to automation
• Increased accuracy of banking transaction
• Convenience
WEAKNESS:
• High cost of service
• Continual wants of customers wants and needs
• Initial investment in technology will be expensive.
OPPORTUNITIES:
• The ability to have a larger customer base
• Global expansion -This is an enormous market which will be a great
opportunity in the future
• The ability to take advantage of the growing opportunity of internet
banking.
• Can achieve customer loyalty and satisfaction
THREATS:
• Continuously changing technology.
• Uncertainty of the banking industry.
• Competition from the lower price operation.
• Possible failure of product due to non-acceptance of customers.
KOTAK MAHINDRA BANK E-BANKING IS
CONVINIENCE-BANKING
In today's day and age time is money. All of us work hard and have a busy
schedule. Doing our banking should be easy, quick and convenient and should
not add to your worries. At Kotak Mahindra Bank, they realize this and have
specially tailored a wide range of value added products and services to make our
money work for us. These, coupled with the highest standards of customer
values, make customers life easier & simpler. Following are various E-
BANKING OPERATIONS carried out by KOTAK BANK. 1) Net Banking
Helps to View details across Accounts, Term Deposits and Demat Accounts -
24x7 Kotak Mahindra Bank's
Net Banking service brings us the timeless world of instant banking. It is quick
and easy, available to us 24X7 and it's absolutely free! Key Features Bank 24X7
- anywhere, anytime Move Money - Within our own Kotak Accounts, to
someone else's Kotak Account, to another bank via NEFT (National Electronic
Funds Transfer/ RTGS (Real Time Gross Settlement) and Demand Draft. We
have the option to 'Pay Now', 'Pay at a later date' or 'Schedule Regular
Payments'. We even have the option to 'Save' the Transaction and pay when
desired. We can even view all your 'Completed Transactions' along with the
status.

We can book a Term Deposit and can do a premature withdrawal online. We
can add a Beneficiary and Multiple accounts can be mapped for a beneficiary
for Transfer Type. (E.g. - NEFT / RTGS etc). Beneficiaries added at other
channels like branch too, will be available for the customer on Net Banking to
make a transfer to. View details across Accounts, Term Deposits and Demat
Accounts. We can Pay our utility bills , VISA Credit Card bills, Recharge
Prepaid Mobile phones and DTH accounts and even pay your Direct tax through
Kotak BillPay Net Banking Features
What all can you do online?
1)Net Banking gives us a host of services, giving us a complete control of our
accounts: View account balance, account activity, place standing instructions
and cheque status Open a Term Deposit Transfer funds online between
your/third party accounts with Kotak Mahindra Bank or any other bank account
via RBI's NEFT or RTGS system Place request for a cheque book, Debit Card
PIN , payment gateway registration and lots more Pay your Utility Bills on
Kotak BillPay Safe online shopping with Kotak Netc@rd View securities
available for Demat View current Mutual Fund holdings, Buy and redeem
Mutual Funds online
2) Kotak Payment Gateway Instant, convenient and secure way of shopping and
making payments online. Kotak Payment Gateway enables us to shop online at
over 5000 websites, make utility bill payments across more than 60 companies
and 42 cities, Following are some of the websites through which you can shop
online. www.bigcinemas.com www.airtel.in www.yatra.com www.vodafone.in
www.makemytrip.com shopping.indiatimes.com Kotak Payment Gateway is an
internet-based facility using which we can pay online merchants by debiting
your selected Bank account. We can pay insurance premium, pay for magazine
subscriptions, make donations to charitable and religious institutions, transfer
money to Kotak Securities for margin money, settlement transfer or IPO
funding. Online Shopping This service enables us to make purchases across
various online shopping sites offering gifts, flowers, airline tickets, exclusive
designer wear, jewellery, latest electronic gadgets / household items,

subscription to books / periodicals, registration to matrimonial, educational sites
or astrology services and much more. Online Trading This service enables us to
transfer money instantly to your account with Kotak Securities, for funding your
margin money or funding our IPO account. An account with Kotak Securities
enables us to buy / sell securities online. This gives us the power of anywhere,
anytime trading.
3) Mobile Banking Experience New-Age Banking. Its all about convenience
banking on our mobile phone. Now, we can experience the benefits of online
banking anywhere and anytime, without the need for a computer. All this
convenience comes to us in a secure and user-friendly application for phones
and tabs on the iOS and Android platforms.
4) Unstructured Supplementary Service Data (USSD) It helps to take command
of our bank account from our GSM mobile phone even without a GPRS
connection. Experience the benefits of banking on the move using USSD.
5) SMS Banking Carry your bank on your phone! Kotak Mahindra Bank's SMS
Banking service enables us to access our bank account, investment account and
demat account on our Mobile Phone. We get latest updates on our account
balance, salary credits, large debits, large credits, holding value and much more,
on our mobile anytime, anywhere. It is quick and easy, available to you 24X7
and it's absolutely free! Key Features We can access our bank account on our
Mobile Phone We can get latest updates of our account balance, salary credits,
and more
6) Alerts We can get Alerts on our mobile or by email for events that we would
like to keep track of. We can subscribe for automatic updates for our account
either on our mobile phone or email address. These alerts are sent on occurrence
of a particular transaction. For example, if the balance in your account falls
below the required Average Quarterly Balance, we get are informed through
ALERTS. Key Features Get automatic updates of our account on either our
mobile or email Get immediate update on a large debit or large credit in to our
account List of Alerts Given below are the Alerts that KOTAK offers: Large

Debit Alert Large Credit Alert Balance below Average Quarterly Balance Alert
Periodic Bank Account Balance - Daily/Weekly (Sent every Monday) Standing
Instruction (SI) Failure Alert
7) Phone Banking Kotak bank’s 24 hr customer service centre is at our service!
Our nearest Kotak Mahindra Bank branch is on your phone. They have a 24-
hour Customer Contact Center to offer us personalized service round the clock.
Just pick up the phone and please call their Center. Whether it is something as
urgent as a stop payment, cash or cheque pickup or we simply want to know our
balance, just give them a call. Their toll free number gives you access to our
account, from anywhere...anytime. And what's more, this facility comes to us
absolutely free of cost! The aim is to save time of customers as they do not have
to visit the branch every now & then for such tasks and facilitates great ease &
convenience. Key Features Quick and easy access from anywhere PIN based
security Customer Care Officers available 24 x 7
8) CARDS Simple. Transparent. Powerful. Secure. Credit Cards NRI Royale
Card, Delight Platinum Card, Fortune Gold Card, Corporate Card etc Debit
Cards Business Class - Gold Debit Card Classic Debit Card Gold Debit Card
Platinum Debit Card Best Compliments Card It lets our loved ones choose their
own gift or shop or enjoy at any place that accepts Visa cards, be it a shopping
mall, a restaurant or a multiplex. Kotak netc@rd Kotak netc@rd is a single use
limited validity online card created by us, from our bank account, at the time of
online shopping and cannot be used after your first payment. It combines the
benefit of using your bank account and the universal acceptance of a VISA Card
in a highly secure environment. It is a one-time credit card. It is a VIRTUAL
CREDIT CARD. It is offered only by Kotak Mahindra bank Kotak World
Travel Card Kotak Mahindra Bank brings us the Kotak World Travel Card, a
prepaid travel card that allows us to forget the hassles of carrying foreign
currency and traveller’s cheques. Now we can be free of the inconvenience of
encashment, potential of misplacement / theft and issues of universal
acceptability

9) ATM Network Their strategically located and constantly growing ATM
network brings the bank within our easy reach. The state of the art touch screen
Kotak Mahindra Bank ATMs are part of the Visa/Plus and Cash net ATM
network. That means you can withdraw cash from their ATM Network with any
International and Domestic Visa/Visa Electron/Plus Credit Cards/Debit Cards.
Key Features Access your account anytime anywhere State of the art Touch
Screen ATMs Affiliated to the VISA network Access any ATM in the country
absolutely free Services available 24-hour access to cash Transfer funds
between accounts View Account Balances and Mini Statement Pin Change
option
10) Cash Deposit Machine Cash Deposit Machine (CDM) is self-service
terminal that enables us to deposit cash without any manual intervention of the
branch officer. Now no need to fill deposit slips and stand in long queues at the
cash counter. Deposit cash through the simple and fast CDM installed in the
branch and we can get instant credit in our account. To use the CDM, we need
to have Kotak Bank Debit Card or know the Kotak Bank's account number in
which we wish to deposit the money. Key Features Instant credit in CASA
account. Immediate receipt. No need to fill cash deposit slips. No need to stand
in long queues. No need to sort and arrange cash denomination wise
11) Cheque Deposit Kiosk Cheque Deposit Kiosk (CDK) is a self-service
terminal that enables us to deposit cheque without any manual intervention of
the branch officer. Now there is no need for us to fill deposit slips and stand in
long queues at the counter. We can deposit our cheque through the simple and
fast CDK installed in the branch. To use the CDK, we need to have 'Kotak
Bank's account' number in which you wish to deposit the cheque. Key Features
Immediate receipt. No need to fill cheque deposit slips. No need to stand in long
queues
12) ASBA: (APPLICATION SUPPORTED BY BLOCK ACCOUNT)
Investing in IPO/FPO/Rights Issue is now simple and convenient through the
new this facility. Key Features Easy to apply in IPO/FPO/Rights Issue over
Phone / Net Banking Enjoy continued Returns on Blocked Amount Place

multiple bids Option to revise/withdraw the bid ASBA facility can also be
availed by High Net-worth Individuals, Corporate, Institutional Investors,
Promoters etc*, along with Retail Investors
13) E-tax: VAT, TDS, CST can be paid online, on monthly basis.
14) OTHERS: Demat services, Funds transfer between own accounts, Third
party transfers to accounts maintained at any branch of KOTAK, Group
Transfers to accounts in KOTAK BANKS, Inter Bank Transfers to accounts
with other Banks, Online standing instructions for periodical transfer for the
above, Request for Issue of Demand Draft, Request for opening of new
accounts, Request for closure of Loan Accounts, Home insurance, Health
insurance, Travel insurance, Motor insurance Card protection plan

MOBILE BANKING FEATURES
a) Banking Services Check balances of your savings & current accounts View
past transactions View / open term deposits Request for account statement,
cheque book or Debit Card PIN Transfer funds (own accounts, Kotak third
party, NEFT, RTGS or IMPS) Make payments without the need to register a
beneficiary through One Time Payment
b) Credit Card View summary of our Credit Cards Pay our Credit Card bills
View statements and unbilled transactions Request for ATM PIN, report loss or
damage of card Balance Transfer Convert transactions to EMIs Request add-on
cards Setup auto debit for our credit card bill payments
c) Bill Pay your bills Make instant payments to our registered billers
d) My Kotak My Kotak is a unique feature, where we can personalize our Home
Page to get all the information of our choice in one place. We can also choose
to view certain information without logging in with MPIN (Mobile Banking
PIN)
e) Service Requests Request for bank account statement Request for cheque
book Status enquiry of your cheque Stop cheque request for Debit Card PIN
Report loss of card Switch primary account of your Debit Card Stop cheque
payment.
f) General We can Change our MPIN. View our profile. List of frequent asked
questions. Kotak Customer Contact Centre numbers under Contact Us and a call
can be made with a simple selection/touch. Links to follow Kotak Mahindra
bank on social media sites (Facebook, You Tube, twitter, etc.).
SECURITY CONCERNS AT KOTAK
How secure is Net Banking?
• Protected by the most stringent security systems, Net Banking allows us to
• transact over a completely secure medium.
• All the transactions travel via 256-bit SSL encrypted medium, the highest
• level of security on the internet.
• The servers are protected with firewalls that make unauthorized access
• impossible.
Kotak Mahindra bank provides 3 main types of securities, they are:
• Each customer is, provided with a User ID( CRN) and Password.
• Our password is generated in such a way that it is only known to us.
• To provide enhanced security and safety they have introduced Dynamic Access Code.
DYNAMIC ACCESS CODE
To log in to Net Banking / Payment Gateway/Mobile Banking we would need to enter an
additional password i.e. your 'Dynamic Access Code'. This Dynamic Access Code is to be
generated online and will be sent instantly to our preferred Email ID and Mobile Number
registered with the Bank.
Dynamic Access Code is valid for an hour from the time it is generated by us. Dynamic Access
Code can be generated by entering our User ID / Nick Name and our Net Banking Password
and clicking on 'Generate Dynamic Access Code' tab on the Dynamic Access Code login page.
For Payment gateway transactions, customers will be required to enter Dynamic Access
Code irrespective of the customer being deregistered for Dynamic Access Code.
Similarly, for creating NetC@rd, registration of Dynamic Access Code is compulsory.

In addition they guard against unauthorized entry or viewing in the following
ways:
To prevent somebody from guessing our password and getting unauthorized access to our
account our User ID is locked in case of three consecutive wrong password entries in 24
hours.
Similarly, to prevent somebody from guessing our Dynamic Access Code and getting
unauthorized access to our account generation of Dynamic Access Code is locked in case of
five consecutive wrong entries of Dynamic Access Code of in 24 Hours.
To prevent an unauthorized person from viewing our Net Banking account in case we leave
our computer idle, they close our Internet session in case of inactivity for an extended period
of time.
We can block our account anytime for any duration we wish by contacting our Customer
Care Officer at our 24-hour Customer Contact Center. It is unblocked upon our request.
To prevent somebody from accessing our Net Banking User ID and Password through
capturing of keystrokes from a keyboard, they have now enabled the 'Virtual Keypad' on the
Net Banking / Payment Gateway Login screen.
Access Code and transaction alerts are sent to our preferred Email ID and Mobile Number
registered with the Bank.
For security reasons, we will not be able to change our preferred Email ID or Mobile Number
through Net Banking and would need to submit a signed request along with an acceptable
proof of identity at your nearest Kotak Mahindra Bank's Branch.
Here are some additional steps that KOTAK MAHINDRA RECOMMENDS to
ensure the security of our transactions:
Password Protection
Changing our password when we receive it the first time, and thereon regularly. Use passwords
that are hard to guess.
Avoid real words or those that can be easily identified, such as, name, family name, date of
birth, telephone number, pet's name, parents' names, etc
Avoid using the same password on different websites.
Always use unique passwords for each website
We should not give our password to or share our password with anybody, including the
employees of Kotak Mahindra Bank.
Notify the Bank immediately by writing to them at [email protected] or calling our
Customer Contact Centre at 1800 102 6022 if we suspect that our password has become

known to or used by someone else.
Login/Browser Security
Always log on to Net Banking by entering the Banks website address www.kotak.com into
the address bar. Do not access the bank website from a link provided in an email from any
source.
Look for the padlock symbol on the bottom bar of the browser to ensure that the site is running
in secure mode before we enter sensitive information. Double clicking on the lock will verify
that the digital certificate is issued to https://www.kotak.com/. Proceed only if
such verification is available
Log off from Kotak Mahindra Bank's Net Banking after we complete our transactions every
time. Do not just close your browser Avoid accessing Kotak Net Banking from a public/shared
computer. In case we need to do so then we should use 'Virtual Key Pad' to input login
credentials
We should regularly log into your Net Banking accounts and check our bank statements to
ensure that all transactions are legitimate
We should clear our browsers cache and history after each session so that our account
information is removed, especially if you are using a shared computer
Configure the browser not to remember passwords (disable Auto Complete function)
Beware of pop-up windows that ask for our account number and PIN (Personal Identification
Number). Kotak Mahindra Bank Login pages are always on a web page and never in a popup
window.
Email Security
Kotak Mahindra Bank will never send e-mails that ask for confidential information. If we
receive an e-mail requesting our Internet Banking details like your PIN, password, account
number etc, please do not respond
"Phishers" typically include upsetting or exciting (but false) statements to get people to react
immediately. Avoid filling out forms in e-mail messages that ask for personal financial
information. Communicate such information only via a secure website
Check the sender E-mail address to verify that it is from a valid E-mail account. Never open
E-mail attachments from sources that you cannot trust
Always scan E-mail attachments for viruses before opening them. If you are unsure about the
source of an attachment, delete it
Be alert for scam E-mails. These are designed to trick us into downloading a virus or
jumping to a fraudulent website and disclosing sensitive information

Computer Security
▪ Make sure your computer has the most recent anti-virus software
▪ Configure the anti-virus software to automatically update the virus definitions
regularly and to notify us when new updates are available
▪ Perform a complete scan of your computer at least once a week
▪ Configure anti-virus software to scan all in-coming and out-going E-mails
▪ Make sure your computers Operating System and browser software are updated with
the latest security patches
▪ Use Anti-Spyware software to do a full system scan to detect any ad/spyware on a
regular basis. Ensure that you update your software regularly
Protect your Information
Our information is the most valuable asset to protect ourself from online fraud such as Identity
Theft. Identity thieves try to obtain key pieces of our confidential information in order to gain
access to our bank account. To protect our confidential information follow below mentioned
steps
▪ Safeguard our account information, just as you would do with any other sensitive
personal information
▪ Do not write our user ID and password anywhere
▪ Always get our latest contact information updated with the bank
▪ Dont carry our Cheque book around with you unnecessarily
▪ Dont leave bill payments or other Cheques in your mailbox
▪ Tear or shred any old Cheques or account statements before throwing them away
Debit/Credit Cards Security
▪ As soon as we receive the consignment carrying your card, ensure that it is in a sealed
▪ condition and not tampered with. If there is any tampering found, inform the bank
immediately
▪ Sign on the reverse of the card immediately on receipt
▪ We should always keep our Debit/Credit card in a safe and secure place. Please inform
the
▪ bank immediately if your Debit/Credit card is lost or stolen, or if you suspect
unauthorized use
▪ Please cut the card diagonally in case it is to be disposed off at the time of
▪ renewal/upgradation/cancellation
▪ We should guard our Kotak Debit/Credit Card's Personal Identification Number (PIN)
like
▪ you guard our cash
▪ Please change Debit/Credit card PIN immediately after overseas trip
▪ Prevent others from seeing you enter your PIN at the ATM by using your body to shield
their view
▪ Memorize your PIN. Don't write it down anywhere, especially on your card, and never
share
▪ it with anyone
▪ Kotak Mahindra Bank recommends that you change your Personal Identification Number
▪ (PIN) every six months

▪ Please destroy and dispose of copies of receipts, airline tickets, travel itineraries and
anything
▪ else that displays your card numbers
▪ When selecting a Personal Identification Number (PIN) don't use any number that
appears in
▪ your wallet (such as name, birth date, or phone number)
▪ NEVER give a photocopy of the front and back of your card to anyone for any reason,
even
▪ if it is an application for a new credit card
▪ Do not hand-over your card to anyone, even if he/she claims to represent the Bank
▪ Never sign a blank application form, to be filled in by an agent or bank representative
later.

RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
1) PROBLEM STATEMENT
The main problem associated with e-banking services are the security concerns
faced by both the banks and their customers. The security concerns like
TROJAN, MALWARE, and PHISING, HACKING, etc, lead to hindrances in
development of e-banking services. The problem also concerns about checking
the satisfaction level of E-BANKING CUSTOMERS AT KOTAK BANK.
2) HYPOTHESIS
• Ho: Gender & Reason to choose E-banking services are not related
• H1: Gender & Reason to choose E-banking services are related.
• Ho: Reason & Purpose to choose E-banking are not related
• H1: Reason & Purpose to choose E-banking are related.
• Ho: Awareness of E-banking risks & precautions of E-banking are not related
H1: Awareness of E-banking risks & precautions of E-banking are related.
• H0: Usage & Precautions of E-banking are not related
• H1: Usage & Precautions of E-banking are related.
• H0: Reason to choose e-banking services & Reason to visit bank are not related
H1: Reason to choose e-banking services & Reason to visit bank are related.
• H0: Type of account& No. Of visits per month are not related
• H1: Type of account& No. Of visits per month are related.
3) OBJECTIVE OF THE STUDY
To study and to make e-banking users aware various e- banking risks like
Phishing, identity theft, frauds of plastic money, Trojan, malware etc. To study
the reasons for the limited use of e-banking services. To create Awareness
among customers towards e-banking services

4) RESEARCH TYPE: DESCRIPTIVE
Descriptive research, also known as statistical research, describes data and
characteristics about the population or phenomenon being studied. Descriptive
research answers the questions who, what, where, when, "why" and how.
5) POPULATION
Population is a set from which samples are drawn. A population can be defined
as including all people or items with the characteristics one wishes to
understand. I have selected the E-banking users of Kotak Bank of Mumbai city.
6) SAMPLE FRAME
Sampling frame is the source material or device from which a sample is drawn.
It is a list of all those within a population who can be sampled, and may include
individuals, households or institutions. For my research purpose I have selected
respondents who are e-banking users of KOTAK BANK.
7) RESEARCH TOOL
Questionnaire consisting of closed ended questions. Google form containing a
set of questions will be submitted to the respondents to gain statistical
information. Unstructured question in which (unlike in a multiple choice
question) possible answers are not suggested, and the respondent chooses from
the given options. The questionnaire also contains a section which has certain
factors which are related to the Likert scale.
8) SAMPLE SIZE
The sample size is 100.
9) SAMPLING TECHNIQUE

Simple Random technique
10) SAMPLING UNITS:
The customers of KOTAK BANK.
11) DATA SOURCE
The Data collected is of the PRIMARY & SECONDARY type.
The PRIMARY data was collected through the QUESTIONNAIRE study. An
GOOGLE FORM was conducted for data collection of E-BANKING.
The SECONDARY data was collected through the website, brochures of the
Kotak Bank, and through research papers on E-banking.
12) EXPECTED CONTRIBUTION OF STUDY
It will contribute significantly, in a positive manner to E-banking users, non e-
banking users & society as they will be aware of the benefits as well as various
risks & threats of e-banking.
13) BENEFICIARIES
E-banking users, non e-banking users & society at large are the beneficiaries as
will be aware of the PROS & CONS of E-banking.

14) SCOPE:
The scope would be wide as we can come across the benefits as well as various
risks & threats of e-banking. To gain accurate results for the study, 100 people
were given questionnaire to know HOW MUCH THEY ARE SATISFIED
WITH THE E-BANKING SEVICES OF KOTAK BANK. The scope of the
study was limited to the customers of KOTAK bank & the city of Mumbai.

LITERATURE REVIEW
1] Dr. Abha Chandra, (July 2010), has carried out a research on
“analytical research on Indian online banking and user’s ‟privacy”, global
journal of enterprise information system.
An empirical study is conducted to evaluate the existence and format of privacy
policies of different banks of India in conducting online banking through their
websites. The objective of this paper is to throw some light on the study,
methodology, and its results. The websites disclose personal information of the
users to Third Parties, which may or may not have their own privacy policies, is
to be counted as one of the reasons for the same. This study also finds that no
Universal Standard format for a Privacy Policy has been designed and declared
for banks in India yet. It will be extremely helpful for net banking consumers, if
there is an authority to monitor and control the proper format and Points
included in the privacy policy for banks.
2] Connel Fullenkamp and Saleh m. Nsouli, (February 2004), have carried
out a research on “six puzzles in electronic money and banking, credit and
banking”, IMF institute.
This paper presents a set of questions or puzzles whose answers will give a
complete picture of electronic money and its impact on the economy. It focuses
on six basic puzzles; these puzzles tend to build on each other. And will help us
in understanding the concept of e-banking.
SIX PUZZLES IN E-MONEY AND E-BANKING:
A. Do We Know What We Are Talking About?
B. What Is Really Different About Electronic Money and Banking?
C. Will Changing Bricks into Clicks Affect the Economy?
D. Gresham's Law Puzzle
E. Monetary Policy without Reserves? Without Money? Without a Clue?
F. Do We Need a Protective Firewall? Can We Build One?

The adoption of Internet e-banking has an important implication for monetary
policy. Monetary policy will become less effective as money holdings become
increasingly interest sensitive, because of Internet e-banking. The impact of this
change has been incremental since the widespread adoption of Internet e-
banking is likely to take place over many years. The paper also states that the
private e-banking activities need to be regulated by the central banks in order to
avoid inflation. This paper provides several important insights into e-money and
e-banking that will be useful to policymakers. It is said that the innovation in e-
banking is the adoption of Internet e-banking, and that the innovation in e-
money is the creation of private e-money. These innovations are the sources of
the most significant effects, including potential problems, from ebanking and e-
money
3] Francisco Javier Miranda, Rosa Cortés and Cristina Barriuso, (2006),
have carried out a research on “quantitative evaluation of e-banking web
sites: an empirical-study of Spanish banks”, the electronic journal
information systems evaluation.
In this there is a discussion regarding the necessary parameters that are needed
in an e banking website. Quality of web home pages was determined using an
original Web Assessment Index, which focuses on four categories: accessibility,
speed, navigability and content. A detailed report of the results arising from this
investigation is presented and systematically analyzed. These findings are useful
for both researchers and practitioners who seek to understand the issues relevant
to electronic banking. In this paper we can say that besides good IT
infrastructure the e banking websites also play an important role in facilitating
the online transactions the language, speed, content etc. play a major role for the
customers to get motivated for using such facilities by the various banks.
4] Hans H. Bauer, Maik Hammerschmidt and Tomas Falk, (2005), have
carried out a research on “International Journal of bank, marketing
Given the fact that banks invest billions in the internet infrastructure (Deutsche
Bank invests approximately half a billion US$ per year), customer satisfaction
and customer retention are increasingly developing into key success factors in
e-banking. Most importantly, profitable ebanking requires a strong focus not

only on the acquisition of new customers but also on the retention of existing
customers. From the study it can be said that the banks should not only focus on
the development of the infrastructure, but also put a large amount of focus on
the convenience provided to their clients, they should be more oriented towards
the satisfaction of their clients and make sure that the clients are more attracted
towards these modern facilities.
5] “Al. I. cuza” Iasi, (2004), has carried out a research on “some issues
about risk management for E banking”, electronic journal of information
systems evaluation
This Study Reveals that In E banking could become the Major Form for
Payment Systems in Organizations as Technologies Will Improve to Create a
Fully Secure Environment. It is believed that e-banking is only a supplement of
traditional methods. This paper suggests that not only is it probable to use e-
banking but that networks especially Internet will promote the quick 5
development of such a services. The paper also suggests the risk associated with
such transactions and the preventions for the same. E-banking presents new
administrative control requirements and potentially increases the importance of
existing controls. Management must evaluate its administrative controls to
maximize the availability and integrity of e-banking systems. E-banking
information can support identity theft for either fraud at the subject institution
or for creating fraudulent accounts at other institutions. It can also be concluded
that both the banks and the customers need to be cautious about what and how
they are dealing with. They must take all necessary precautions while using such
technology.
6] Dospinescu Octavian, Rusu Daniela, “AlexandruIoan Cuza”,(2006),
have carried out a research on “ the adoption of electronic banking services
in developing countries – the Romanian case” information systems
The developments taking place in information and communication technology
are affecting the financial institutions worldwide. This evolution had
transformed the way banks deliver their services, using technologies such as
automated teller machines, phones, the Internet, credit cards, and electronic
cash. In this scenario, banking in Romania had undergone some changes. Many

banks have been investing in Internet technology in order to maintain a
competitive edge and satisfy their customers. The Internet, phone, mobile or
electronic banking offered in the Romanian banking market is in full
development process, and the banks have to win the confidence of the individual
and corporate body customers, taking into account the fact that the transactions
that are made on the online system are perceived as highly risky, But the level
of accessibility regarding the performing of banking operations straight from the
company office or from home without depending on the opening hours of pay-
offices determines a growing number of customers to resort to this kind of
services.
7] Dr. Asma Mobarek, (2004), has carried out a research on “e-banking
practices and customer satisfaction- a case study in Botswana”,
international journal of bank marketing
This research involves the study of four commercial banks in Botswana, these
being – Standard Chartered Bank, First National Bank, Barclays Bank and Bank
of Baroda. All these banks are providing e-banking services to their customers.
The usual E-banking services provided by banks are account management; bill
payment and presentment; new account opening; consumer wire transfers;
investment/brokerage services; loan application and approval; account
aggregation; cash management ; small business loan applications, approvals, or
advances; commercial wire transfers; business-to-business payments; employee
benefits/pension administration etc. The paper includes an analysis of
customers‟ perception towards e-banking services, the quality of ebanking
services provided by the banks and the constraints in achieving customer
satisfaction. The focus of the paper particularly on four delivery channels
namely: Automated Teller Machine (ATM), internet banking, tele-banking and
manual banking. The main focus is done on internet banking as it is the delivery
channel that seems to be slowly growing in Botswana after the ATM delivery
channel. Consumer behavior is changing partly because of less spare time. The
way of use of financial services is classified by individuality, mobility,
independence of place and time and flexibility. Financial transactions caused by
purchases will more and more be carried out by non- and near- banks. These
facts represent big challenges for banks. Banks are using the Internet as a new

distribution channel. The hypotheses are tested and show that there is a
relationship between age group, occupation type and some aspects of e-banking.
At last that Banks must adapt to the electronics age. Consumers demand it.
Economics drives it. Banks must exploit it.
8] Dr.S. Arumugaperumal, (July 2006), has carried out a research on
“impact of cyber crime on virtual banking”. Journal Computer Science-
S.T.Hindu college, Nagercoili
This paper basically deals with the online risks that the banks and their clients
face during the online transactions they undertake. As more organizations
provide greater online access for their customers, professional criminals are
successfully using phishing techniques to steal personal finances and conduct
identity theft at a global level. The popularity which virtual banking services
have won among customers, owning to the speed, convenience and continuous
access they offer, is likely to increase in the future. However, several issues of
concern would need to be pro-actively attended. While most of electronic
banking has built-in security features such as encryption, prescription of
maximum monetary limits and authorizations, the system operators have to be
extremely vigilant and provide clear-cut guidelines for operations. On the larger
issue of electronically initiated funds transfer, issues like authentication of
payments instructions, the responsibility of the customer for secrecy of the
security procedure would also need to be 7 addressed. So for the better security
multifactor authentication is best to make the virtual banking much safer with
higher security in the coming years.
9] Gautam Ivatury & Ignacio Mas, (April 2008), have carried out a
research on “the early experience with branchless banking.” focus note 46.
Washington, D.C. CGAP
Branchless banking has great potential to extend the distribution of financial
services to poor people who are not reached by traditional bank branch
networks; it lowers the cost of delivery, including costs both to banks of building
and maintaining a delivery channel and to customers of accessing services (e.g.,
travel or queuing times)

10] Basel committee on banking supervision, (may2001), has carried out a
research on “risk management principles for electronic banking,
“electronic banking group initiatives and white papers”.
Banking organizations have been delivering electronic services to consumer’s
and Business for years. Electronic funds transfer, including small payments and
corporate cash management systems, as well as publicly accessible automated
machines for currency withdrawal and retail account management, are global
fixtures. This study explains a clear need for more work in the area of e-banking
risk management and that mission was entrusted to a working group comprised
of bank supervisors and central banks, the Electronic Banking Group (EBG),
which was formed in November 1999
OBSERVATIONS:
1. Branchless banking can dramatically reduce the cost of delivering financial
services to poor people.
2. Branchless banking channels are used mainly for payments, not for savings
credit.
3. Few poor and unbanked people have begun using branchless banking for
financial services.
4. Financial services providers view agent networks as key to achieving their
business strategy.
5. Most mobile banking projects to extend market reach have been led by mobile
operators.

PREDICTIONS:
1. Poor people will use mobile banking more than rich people.
2. Providers will manage the operational risks of using Agents, and customers will
tolerate liquidity shortfalls.
3. Shared agent networks will be the key to massively expanding access to finance
through branchless banking.
4. Mobile banking will be used by large numbers of poor, currently unnerved
people in about three years, as a result of competitive market entry
Principles of e banking:
1. Effective management oversight of e-banking activities.
2. Establishment of a comprehensive security control process.
3. Comprehensive due diligence and management oversight process for
outsourcing relationships and other third-party dependencies.
4. Authentication of e-banking customers.
5. Non-repudiation and accountability for e-banking transactions
6. Appropriate measures to ensure segregation of duties.
7. Proper authorization controls within e-banking systems, databases and
applications.
8. Data integrity of e-banking transactions, records, and information.
9. Establishment of clear audit trails for e-banking transactions.
10. Confidentiality of key bank information.
11. Appropriate disclosures for e-banking services.
12. Privacy of customer information.
13. Capacity, business continuity and contingency planning to ensure availability of
e banking systems and services.
14. Incident response planning
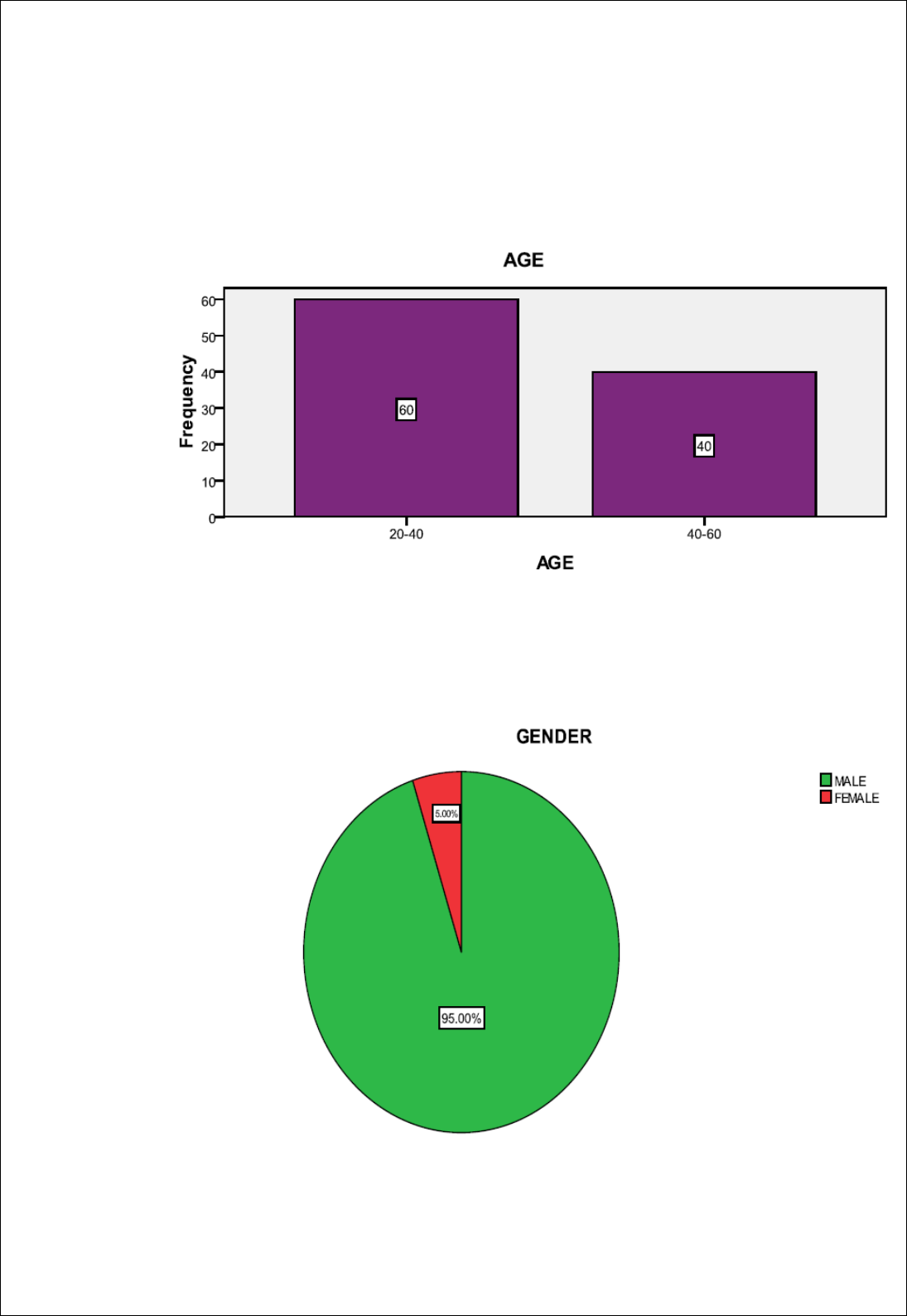
DATA ANAYLYSIS
1) AGE GROUPS USING E-BANKING SERVICES
2) THE USE OF E-BANKING SERVICES BASED ON THE GENDER
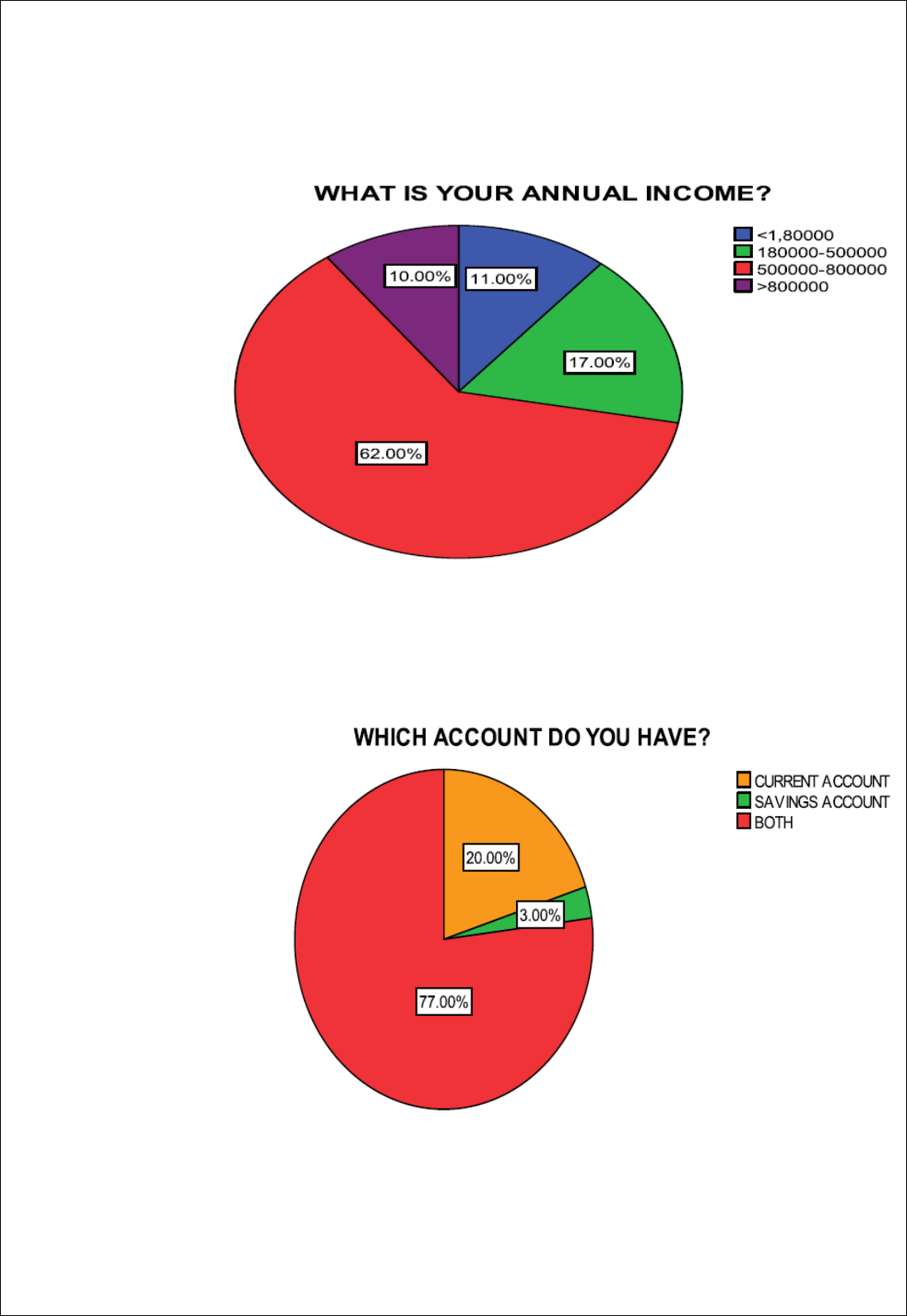
3) ANNUAL INCOME OF E-BANKING USERS
4) WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING ACOUNTS DO YOU HAVE WITH
YOUR BANK?
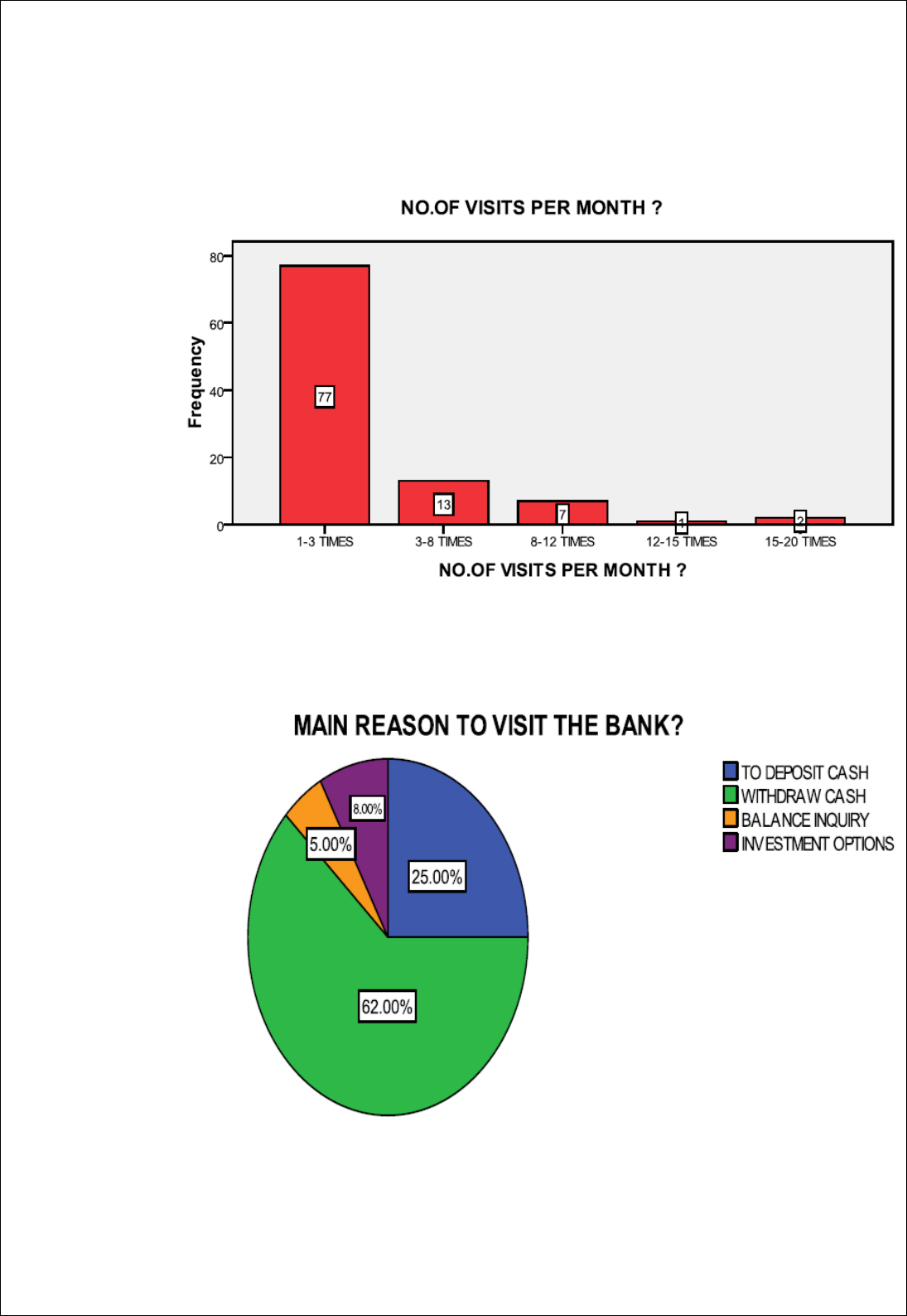
5) HOW FREQUENTLY DO YOU VISIT YOUR BANK BRANCH PER
MONTH?
6) WHAT IS THE MAIN REASON THAT YOU TYPICALLY VISIT YOUR
BANK BRANCH
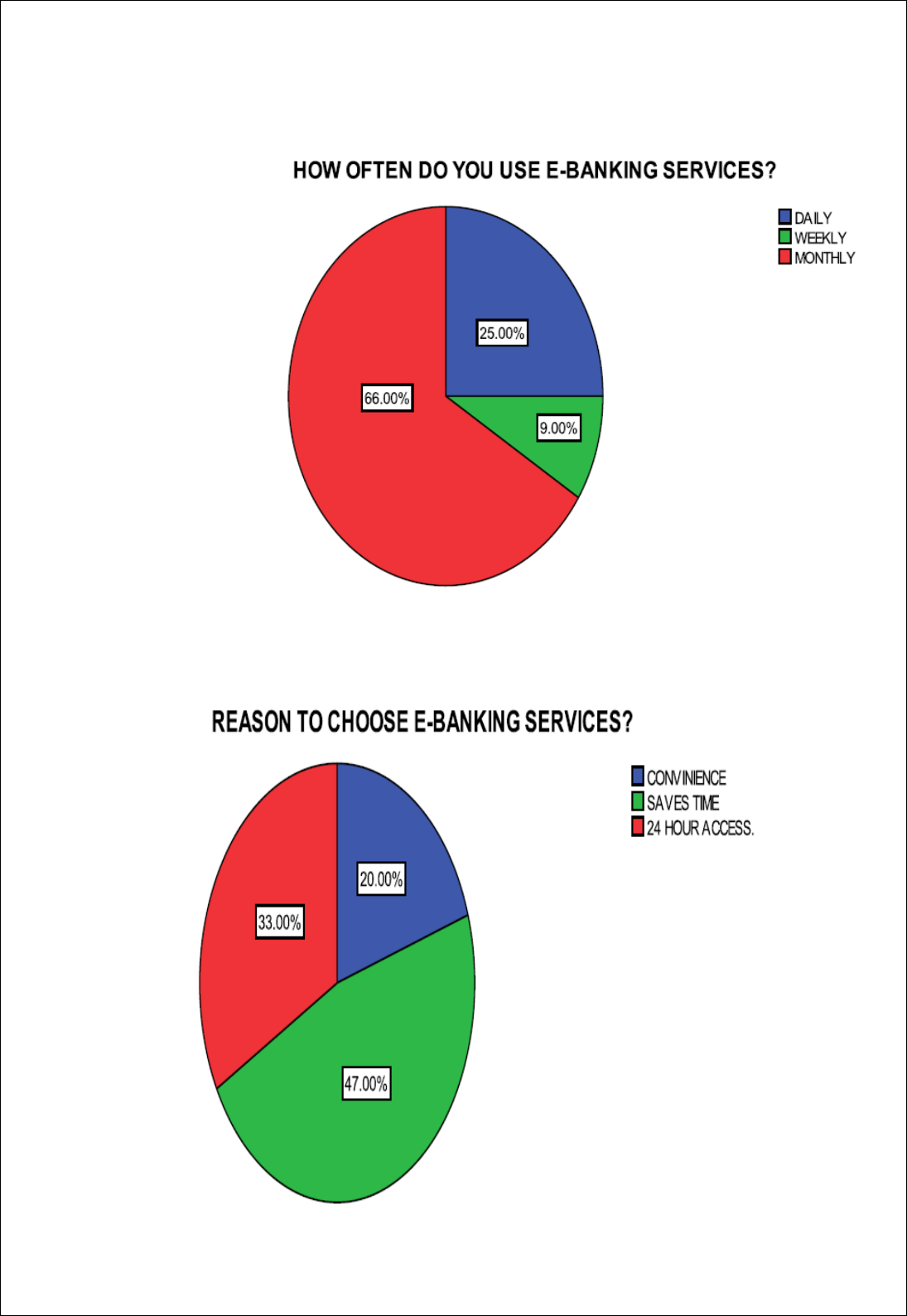
7) HOW OFTEN DO YOU USE E-BANKING SERVICES?
8) WHAT ARE THE REASONS FOR CHOOSING E-BANKING
SERVICES?
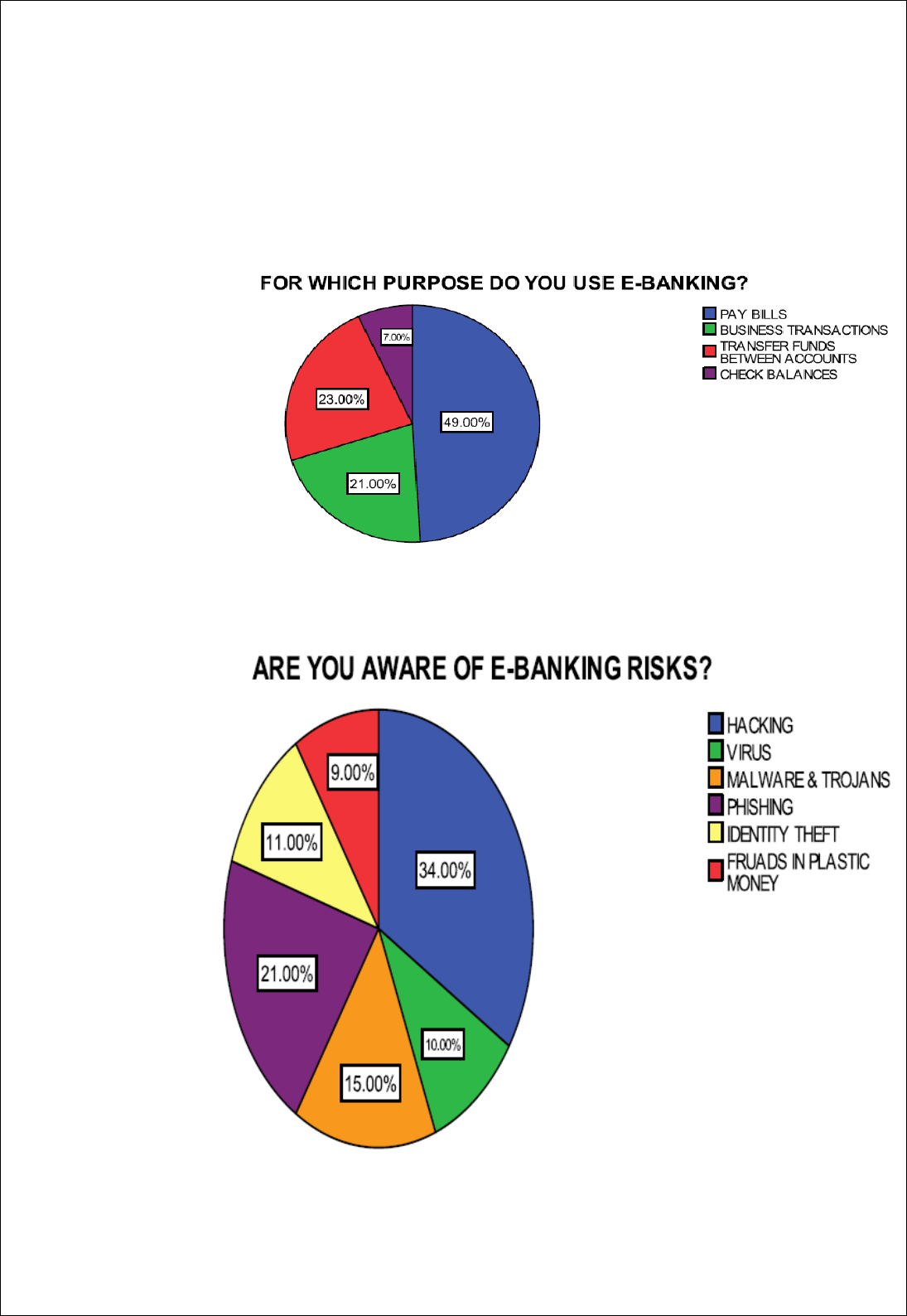
9) FOR WHICH PURPOSE DO YOU USE E-BANKING SERVICES
REGULARLY?
10) ARE YOU AWARE OF THE FOLLOWING E-BANKING RISKS?
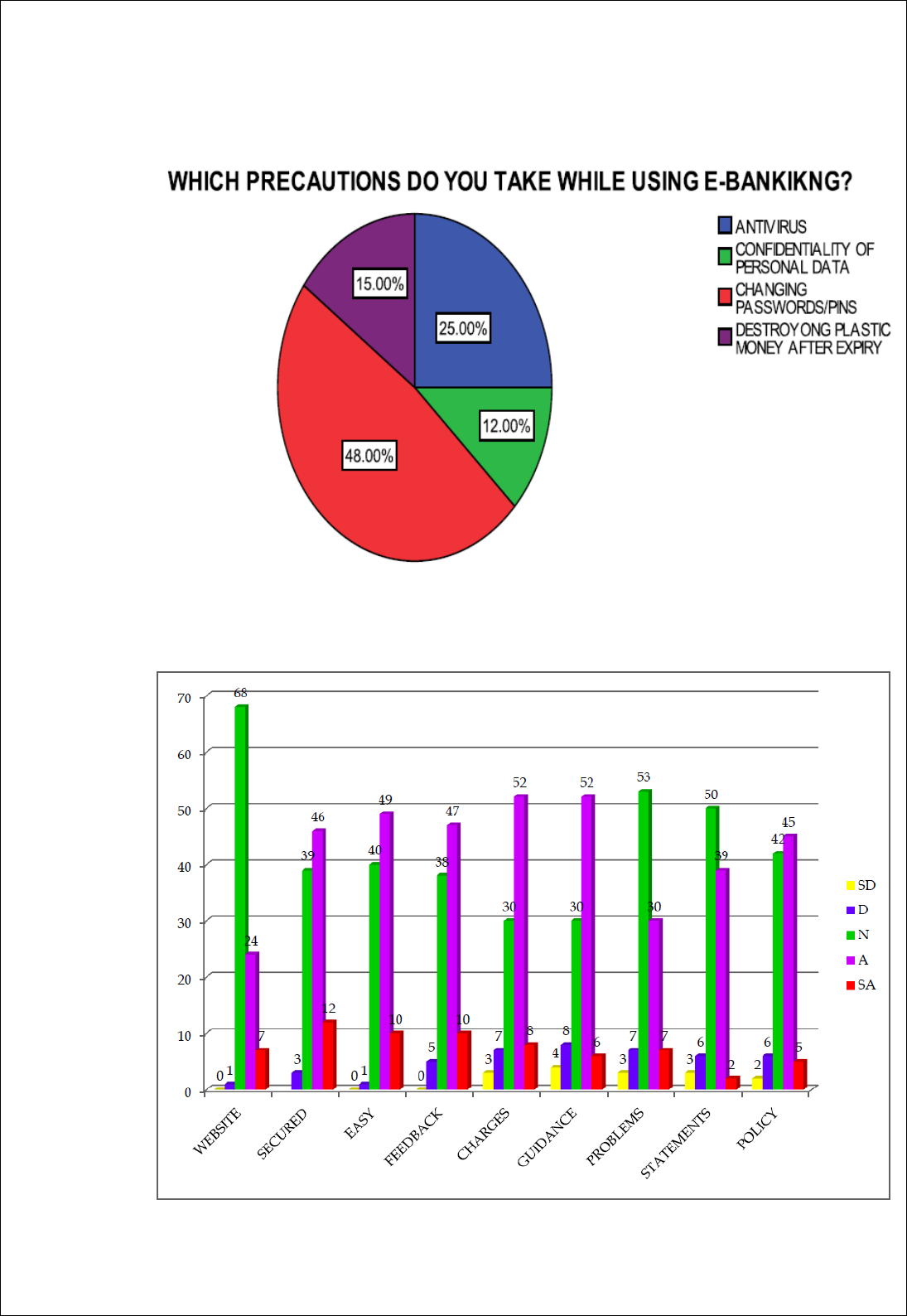
11) WHAT PRECAUTIONS DO YOU TAKE WHILE USING E-BANKING
SERVICES?
12) HOW SATISFIED ARE YOU WITH E-BANKING SERVICES
PROVIDED BY KOTAK?
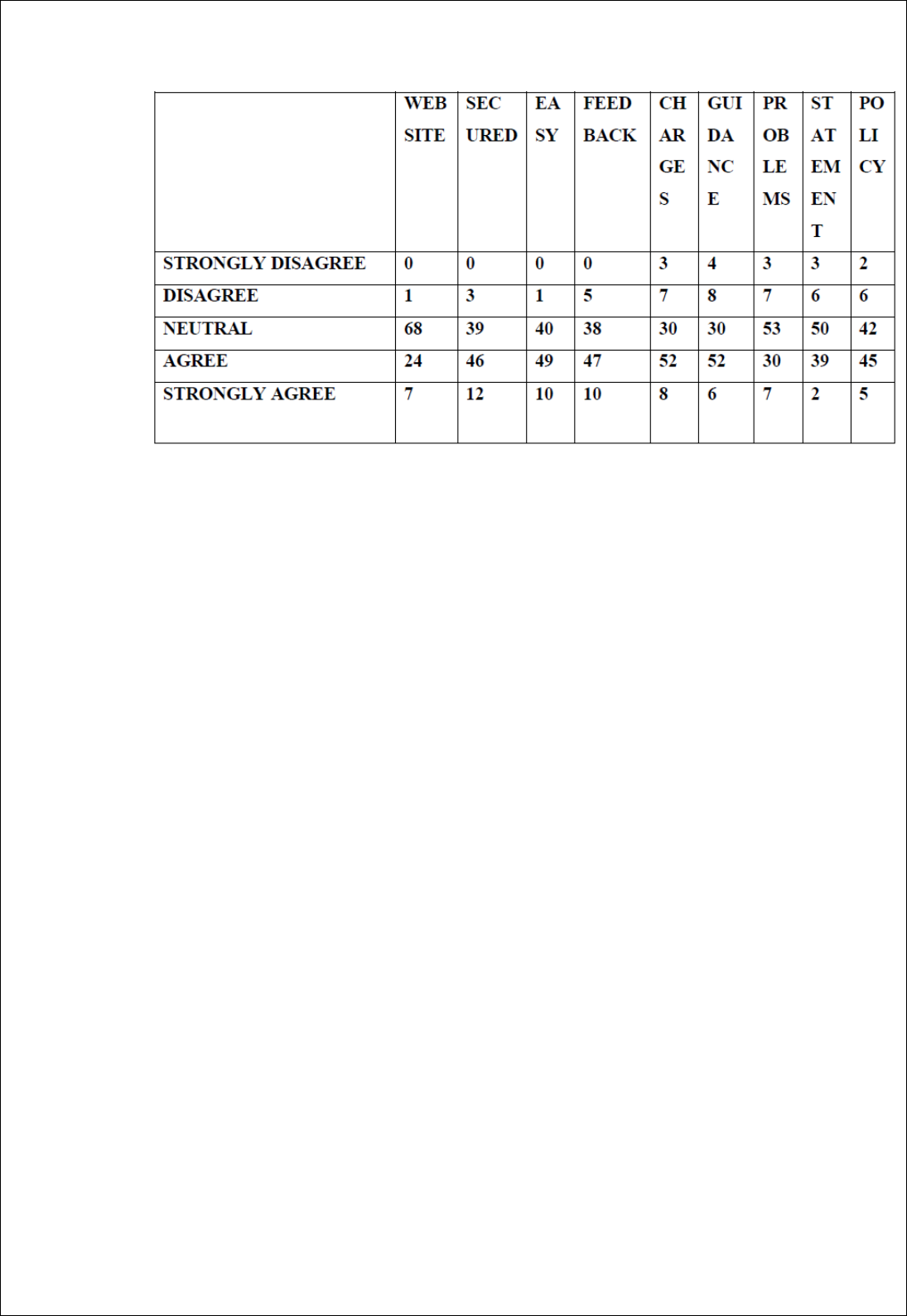
INTERPETATION:
• Website: e-banking websites are quick to access has a neutral view from
customers.
• Secured-banking users agree that e-banking transactions are secured.
• Easy: majority of customers agree that using e-banking services is easy.
• Feed back: majority of e-banking users feel that they are given the required
feedback
• immediately.
• Charges-banking charges are reasonable, majority of them agree to it
• Guidance: all users agree that bank provides necessary guidance as & when
needed.
• Problems: problems are solved quickly & immediately has a neutral view from
users
• Statements: banks provide the users needed statements has a neutral view.
• Policy: policy framed by banks protects the e-banking users is agreed by
majority of users.
Overall, the e-banking users have either agreed or have a neutral view towards
above stated Criteria’s; degree of disagreement is comparatively very low &
only in few categories, & the degree of strongly disagree negligent & found in
criteria’ s like-banking charges are too high, problems are not solved promptly,
guidance to use E-banking services is not provided by bank, bank does not
provide statements, the policy framed does not protect customer interest etc.

ONE-VARIABLE ANALYSIS OF QUESTIONNAIRE
1) AGE GROUPS USING E-BANKING SERVICES
It is observed that only two age groups ranging, from 20 to 40 and 40-60 years
out of four are users of E-banking services. From this we can conclude that even
the preceding generation is becoming more & more aware of benefits &
convenience of E-banking.
2) THE USE OF E-BANKING SERVICES BASED ON THE GENDER
From the response of the individuals, it was observed that the number of male
users is more than female users with respect to the use of e-banking services.
One of the reasons could be that men are more into commercial use of the e-
banking products than the females. It could also be possible that there may be a
limited use of the e-banking services in case of females.
3) WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING ACOUNTS DO YOU HAVE WITH
YOUR BANK?
From the data collected majority of customers had both current & savings a/c at
Kotak bank. So customers are concerned with savings as well as carrying out
business transactions smoothly from one branch only
4) HOW FREQUENTLY DO YOU VISIT YOUR BANK BRANCH PER
MONTH?
Majority of e-banking users visit the bank at the most 1-3 times a month.
Majority of e-banking users visit the bank at the most 1-3 times a month. This
basically shows the potential of high degree of development E-banking services
& also, awareness regarding its ease, time saving and convenience is now wide
spread.
5) WHAT IS THE MAIN REASON THAT YOU TYPICALLY VISIT YOUR
BANK BRANCH?
From the data collected most of the customers mainly visit the bank for
withdrawal of cash.
6) HOW OFTEN DO YOU USE E-BANKING SERVICES?
Majority of e-banking users use e-banking services monthly. The reason may be
for paying their monthly bills like telephone bill, electricity bill mobile bill,
online tax payment VAT, TDS, CST on monthly basis. Etc.
7) WHAT ARE THE REASONS FOR CHOOSING E-BANKING
SERVICES?
From the e-banking users questioned majority of them choose e-banking
services as it saves their time. Time is what majority of us don’t have in our

busy schedule. Second main reason is that is has a 24 hour access so at any point
of time we can update ourselves with whatever information we want
8) FOR WHICH PURPOSE DO YOU USE E-BANKING SERVICES
REGULARLY?
Majority of e-banking users use this service regularly for payment of their
monthly bills, Kotak offers monthly payment of mobile, telephone, electricity
bill & online tax payment -VAT, TDS, CST
9) ARE YOU AWARE OF THE FOLLOWING E-BANKING RISKS?
Majority of e-banking users are aware of Hacking, and least is known to them
of frauds of plastic money i.e ATM, CREDIT/DEBIT CARD. Other risks are
well known to them.
10) WHAT PRECAUTIONS DO YOU TAKE WHILE USING E-BANKING
SERVICES?
As a precaution against e-banking risks majority of e-banking users periodically
keep on changing their PIN/PASSWORDS. And that is what the Kotak bank
recommends & suggests every now & then to its E-banking users.
11) HAVE YOU BEEN VICTIM OF E-BANKING FRAUDS THROUGH
KOTAK BANK?
Out of e-banking users surveyed no one had been a victim of e-banking frauds
through Kotak Mahindra bank. The reason is - All the transactions travel via
256-bit SSL encrypted medium, the highest level of security on the internet
12) HOW SATISFIED ARE YOU WITH E-BANKING SERVICES
PROVIDED BY KOTAK BANK?
Overall, the e-banking users have either agreed or have a neutral view towards
above stated criteria’s; degree of disagreement is comparatively very low & only
in few categories, & the degree of strongly disagree negligent & found in
criteria’s like, E-banking charges are too high, problems are not solved
promptly, guidance to use E-banking services is not provided by bank, bank
does not provide statements, the policy framed does not protect customer
interest etc.

CONCLUSION
From the research conducted by us we derive several conclusions:
1) It is observed that AGE plays an important role with respect to the use of e-
banking services. It is found that the senior citizens are less comfortable with
use of these services. It is observed that only two age groups ranging, from 20
to 40 and 40-60 years out of four are users of E-banking services. From this we
can conclude that even the preceding generation is becoming more & more
aware of benefits & convenience of E-banking
2) With respect to the literacy level it is observed that majority of customers have
knowledge of limited aspects of information technology.
3) None of customers were affected with e banking threats, which shows a positive
sign towards the development of these services.
4) From the study it is observed that customers are willing to use modern banking
facilities having given them adequate guidance and security measures by bank.
5) With respect to the frequency of visits it is observed that customers make
frequent visit to banks which can be minimized with optimum provision of e
banking services.
LIMITATIONS OF STUDY
1) The sample size was 100 which was not covering the entire geographical area
of Mumbai & entire population of E-banking users of Kotak Mahindra Bank so
there is a possibility that there may be variations in the results obtained.
2) During the data collection the respondents did not fill the questionnaire
genuinely, for instance the respondents who were not using the e-banking
services have attempted the segments that were framed for the users of the e-
banking services. Due to this there may be variations in the results obtained.
3) The respondents restricted themselves from answering the questions mentioned
for the fear of letting their views disclosed to others
RECOMMENDATIONS
From the response of the individuals it was observed that the number of male
users is more than female users with respect to the use of e-banking services. It
could be possible that there may be a limited use of the e-banking services in
case of females. So the female gender should be made more & more aware of
E-banking benefits, ease, convenience, precautions, risks, threats etc E-banking
users should be made more & more aware of E-banking risks & threats and also
how to safeguard themselves against the same by taking precautions &
following SECURITY GUIDELINES issued by their banks. E-banking users
should NEVER TAKE THEIR BANKS FOR GRANTED for their security,
because YOUR SECURITY IS (Y)OUR RESPONSIBILITY-KOTAK
MAHINDRA BANK.

BIBLIOGRAPHY
• “Al. I. cuza” Iasi, (2004), some issues about risk management for E banking,
electronic journal of information systems evaluation ,volume 9, issue 2, pp 73-
82.
• Basel committee on banking supervision, (may2001), risk management
principles for electronic banking, “electronic banking group initiatives and
white papers”.
• Connel Fullenkamp and Saleh m. Nsouli, (February 2004), six puzzles in
electronic money and banking, credit and banking, IMF institute, vol. 34, pp
112-123.
• Dospinescu Octavian, Rusu Daniela, “AlexandruIoan Cuza”, (2006), “the
adoption of electronic banking services in developing countries – the Romanian
case information systems”, vol 2, pp 34-67.
• Dr. Abha Chandra, (July 2010), analytical research on Indian online banking
and users‟ privacy, global journal of enterprise information system, vol.2
isssue.1.
• Dr. Asma Mobarek, (2004), e-banking practices and customer satisfaction- a
case study in Botswana, international journal of bank marketing, vol. 21, pp 94
– 103.
• Dr.S. Arumugaperumal, (July 2006), Reader and Head Department of Computer
Science S.T.Hindu college, Nagercoil-2.
• Francisco Javier Miranda, Rosa Cortés and Cristina Barriuso, (2006),
quantitative evaluation of e-banking web sites: an empirical-study of Spanish
banks, the electronic journal information systems evaluation volume 9 issue 2,
pp 73 – 82.
• Gautam Ivatury & Ignacio Mas, (April 2008), the early experience with
branchless banking.” focus note 46. Washington, D.C. CGAP.
• Hans H. Bauer, Maik Hammerschmidt and Tomas Falk, (2005), International
Journal of bank, marketing, vol. 23 no. 2, pp. 153-175
